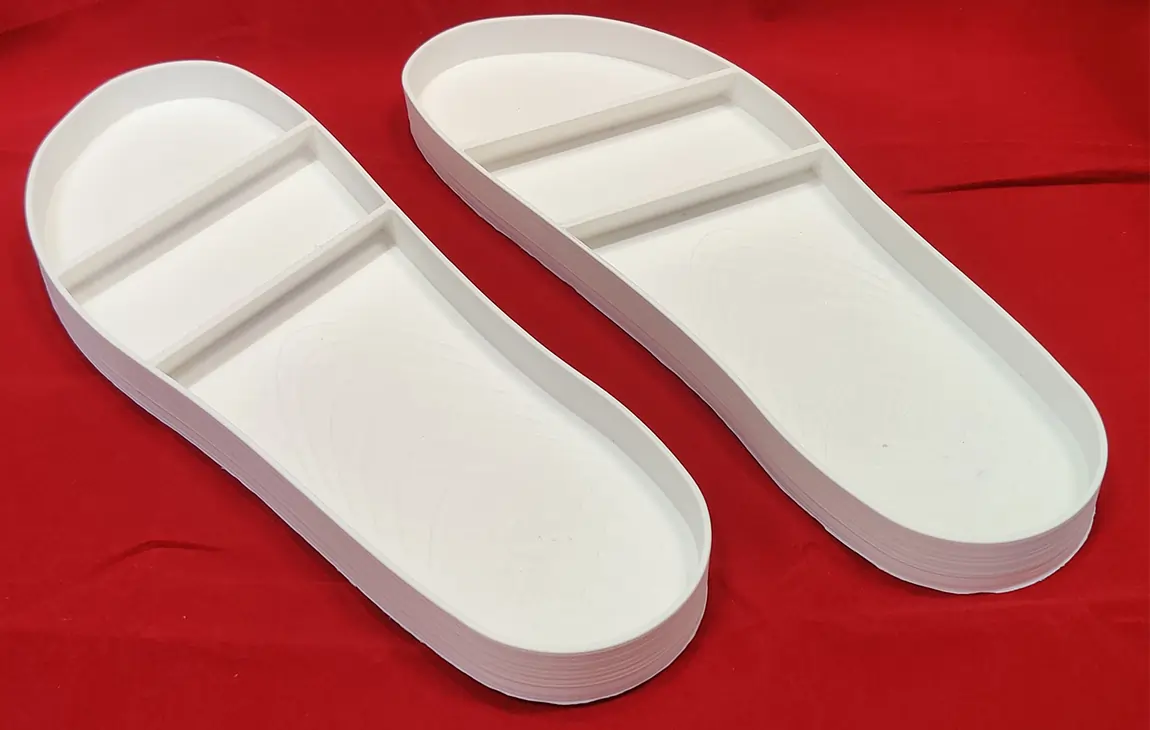
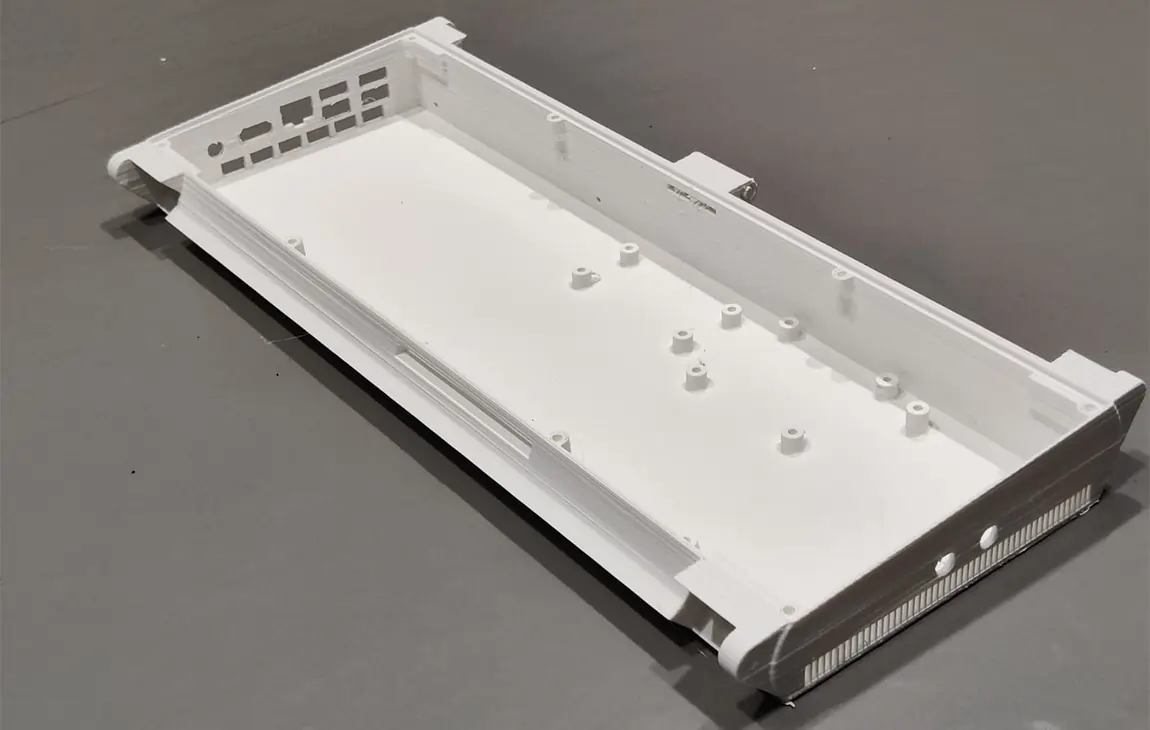
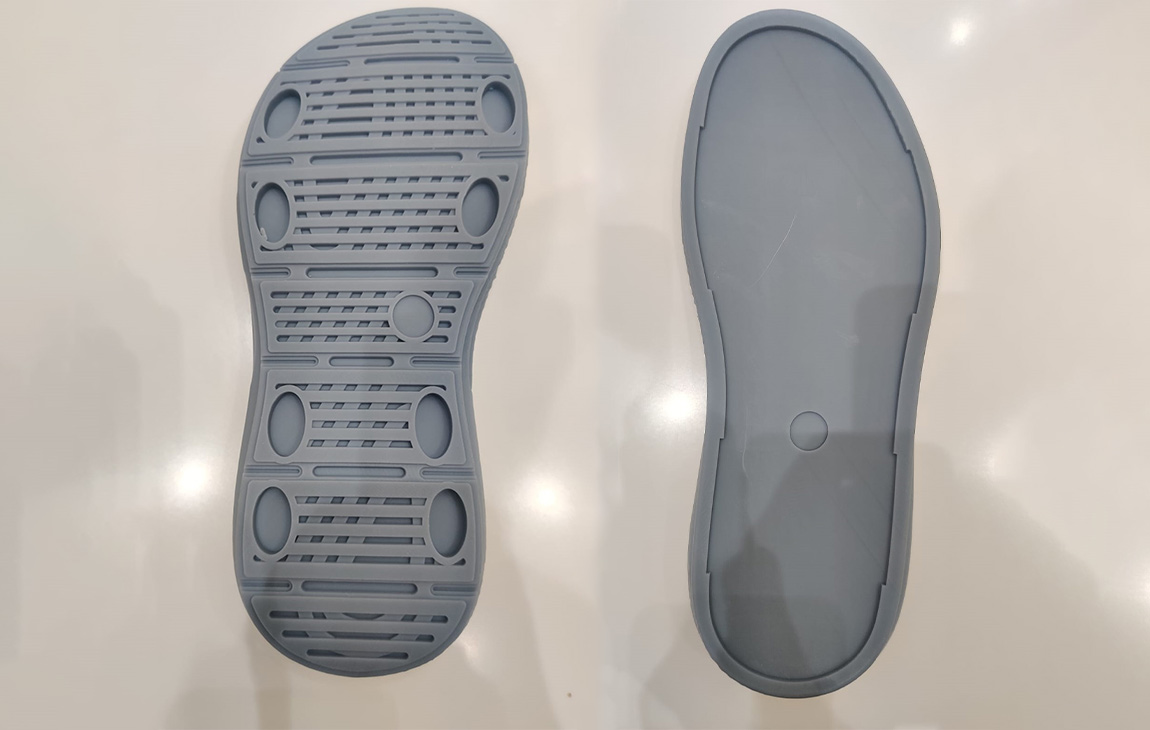
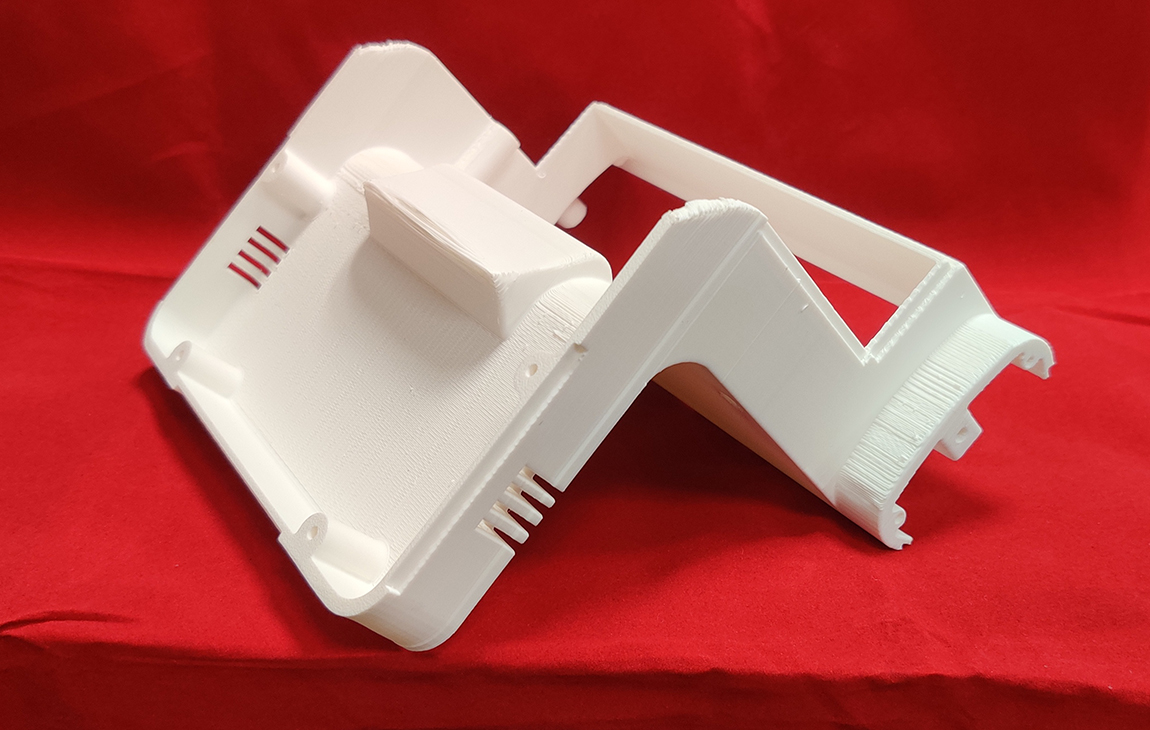
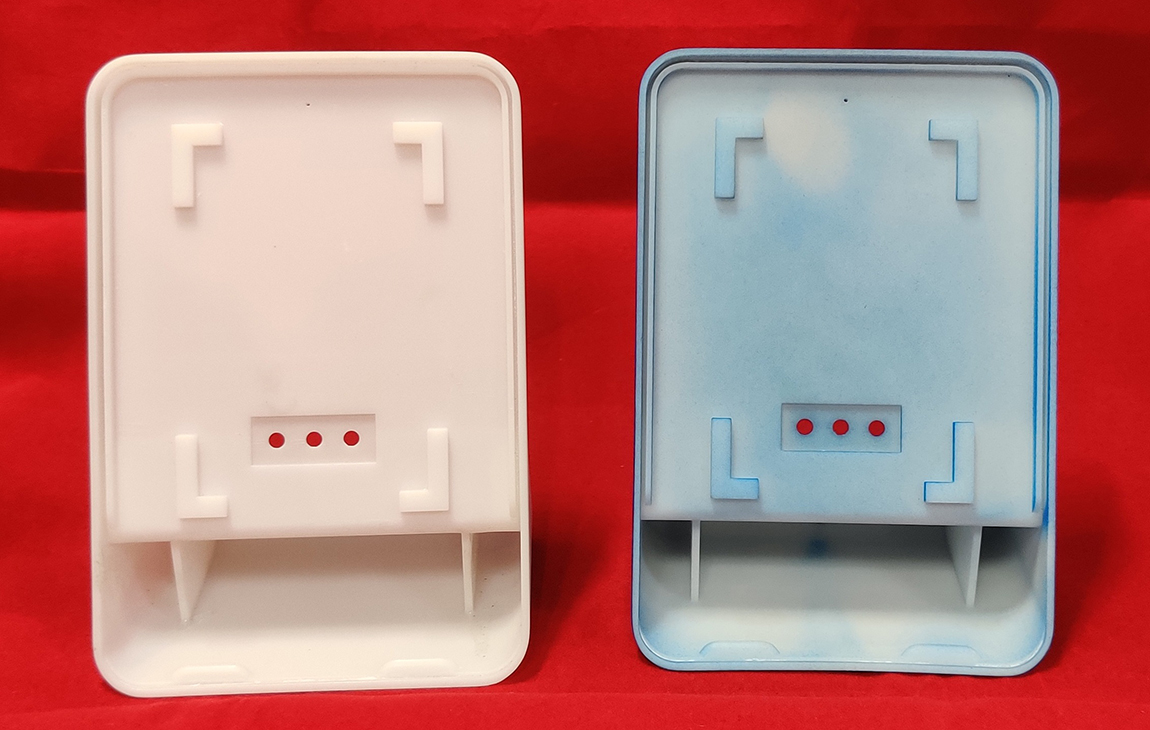
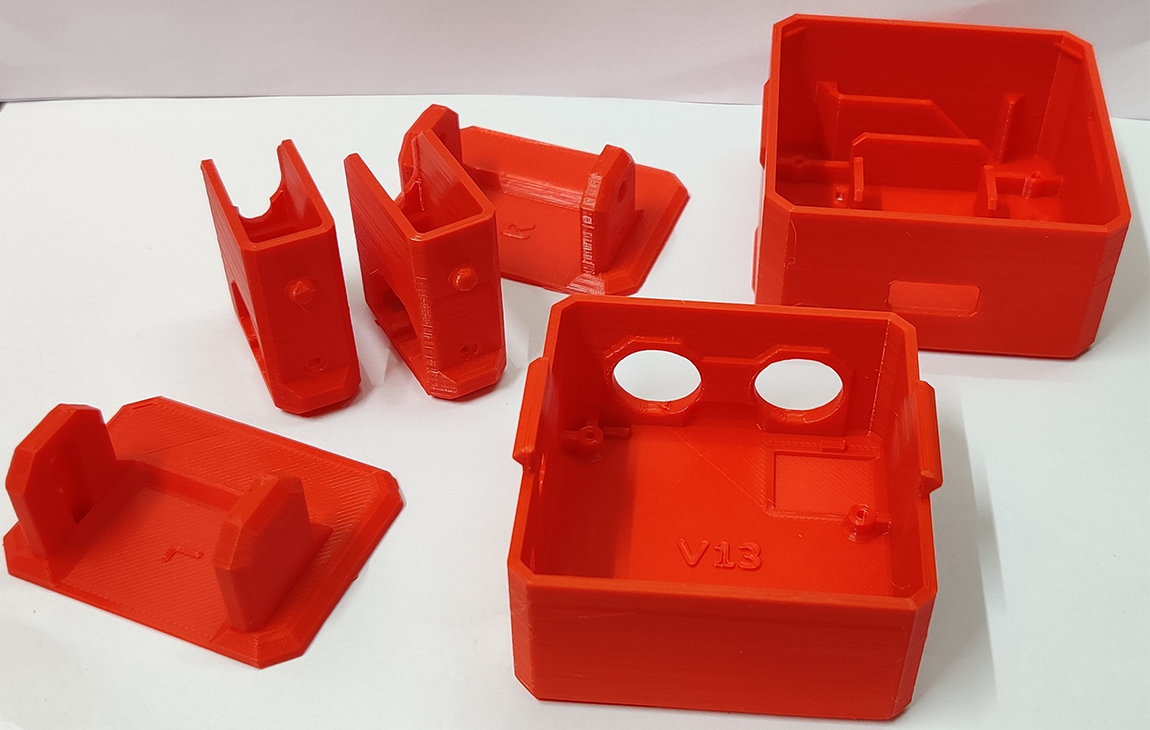
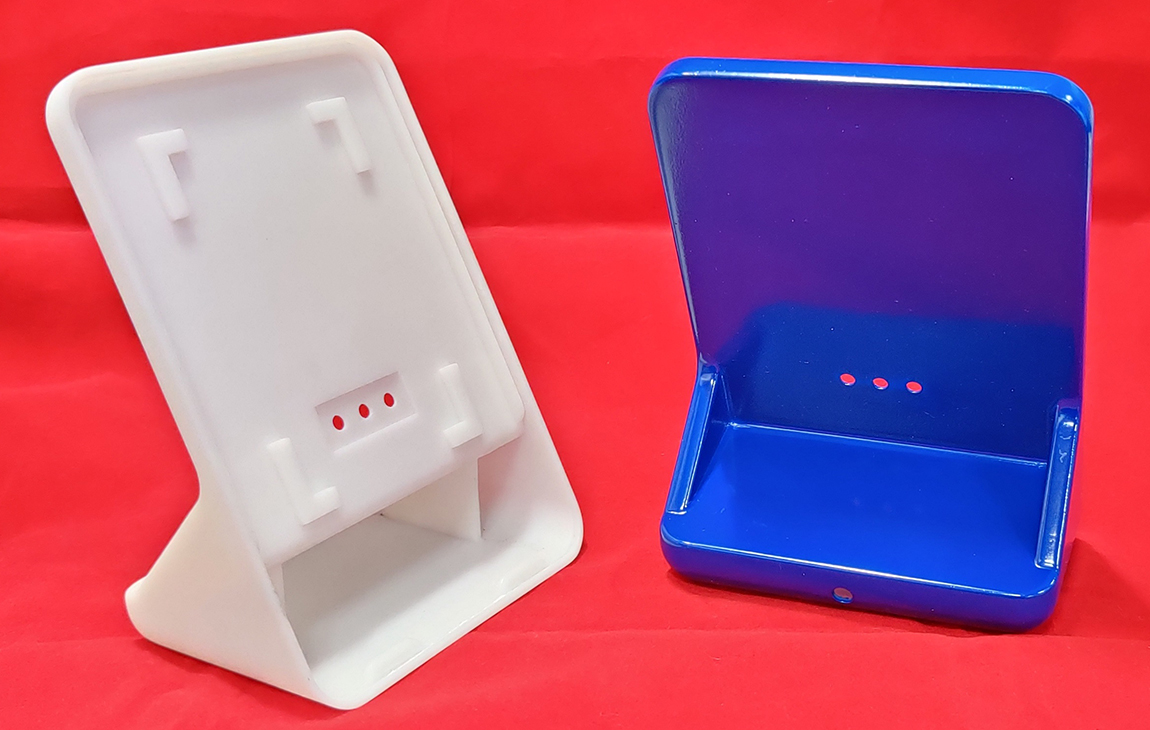
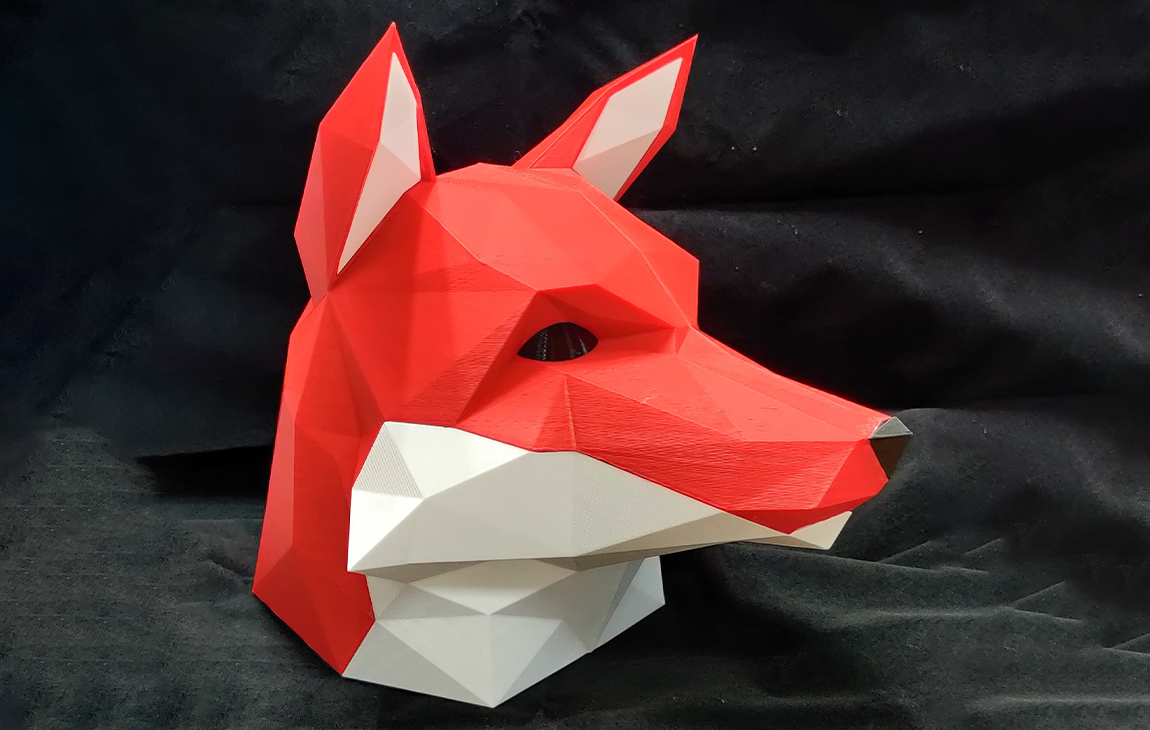
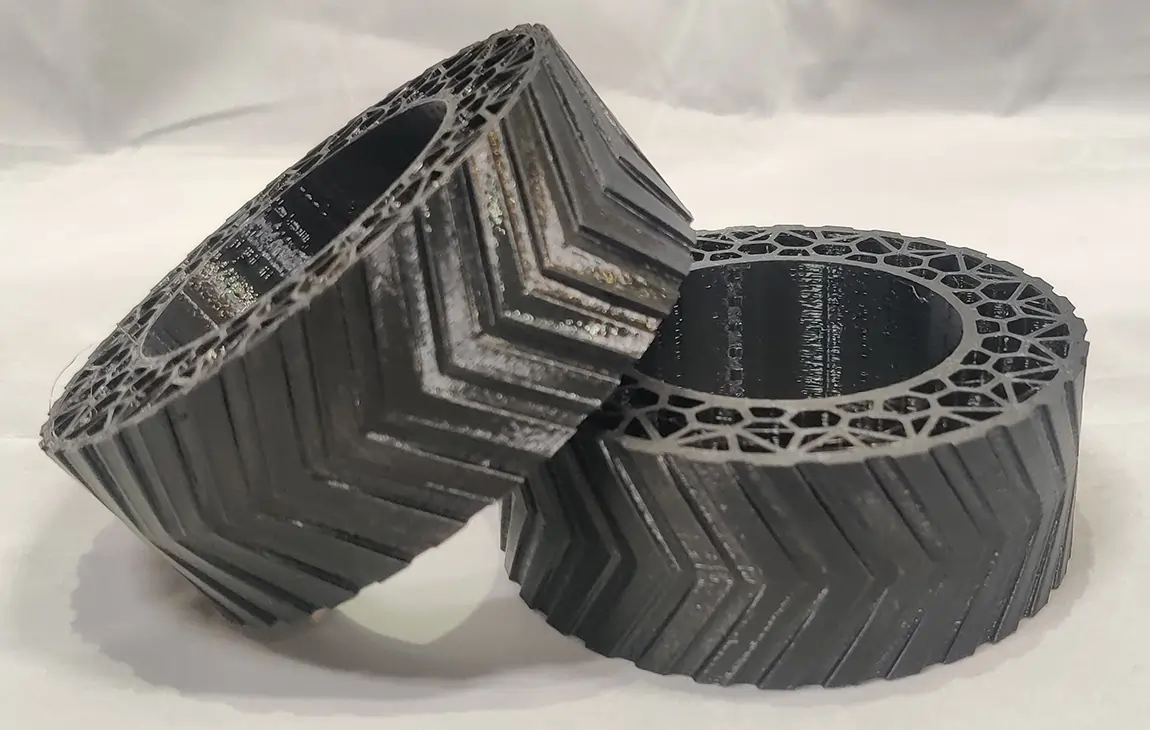
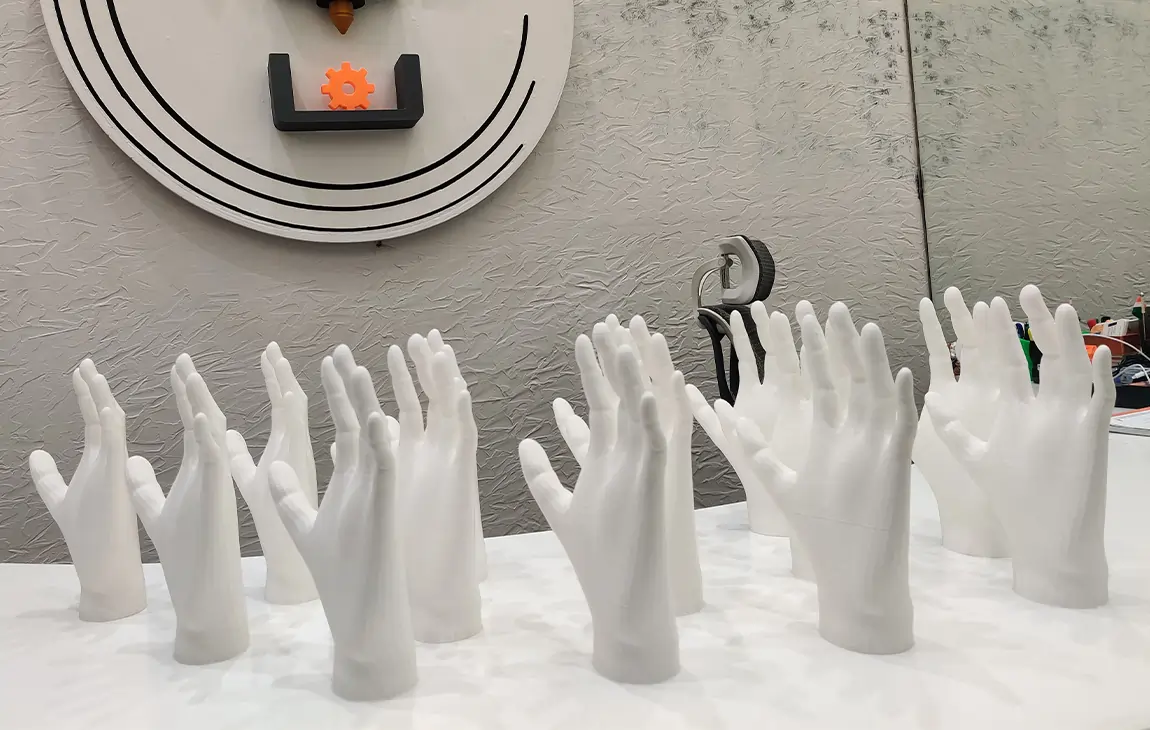
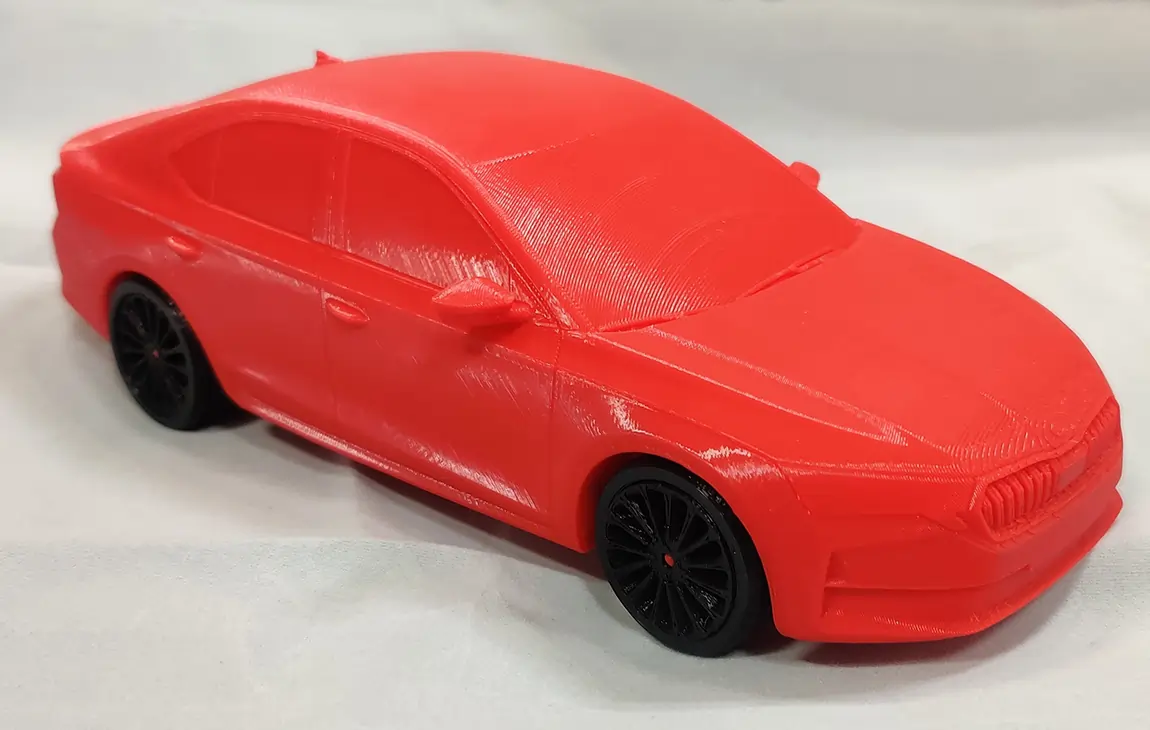
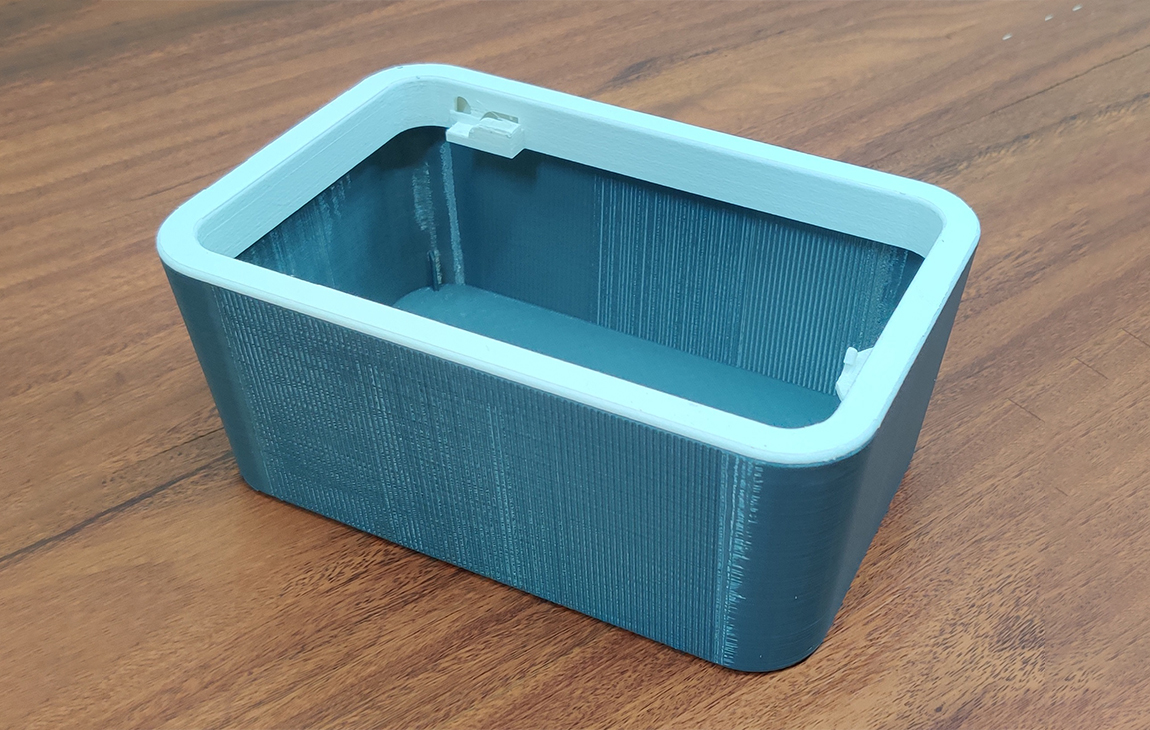
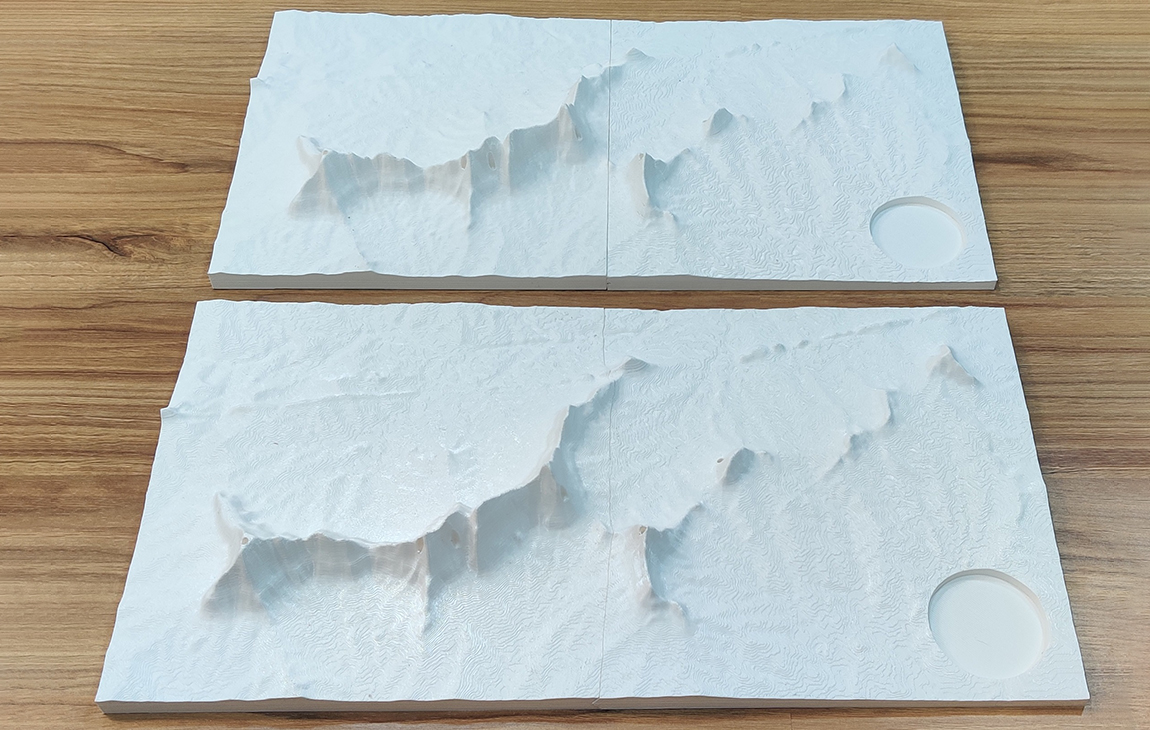
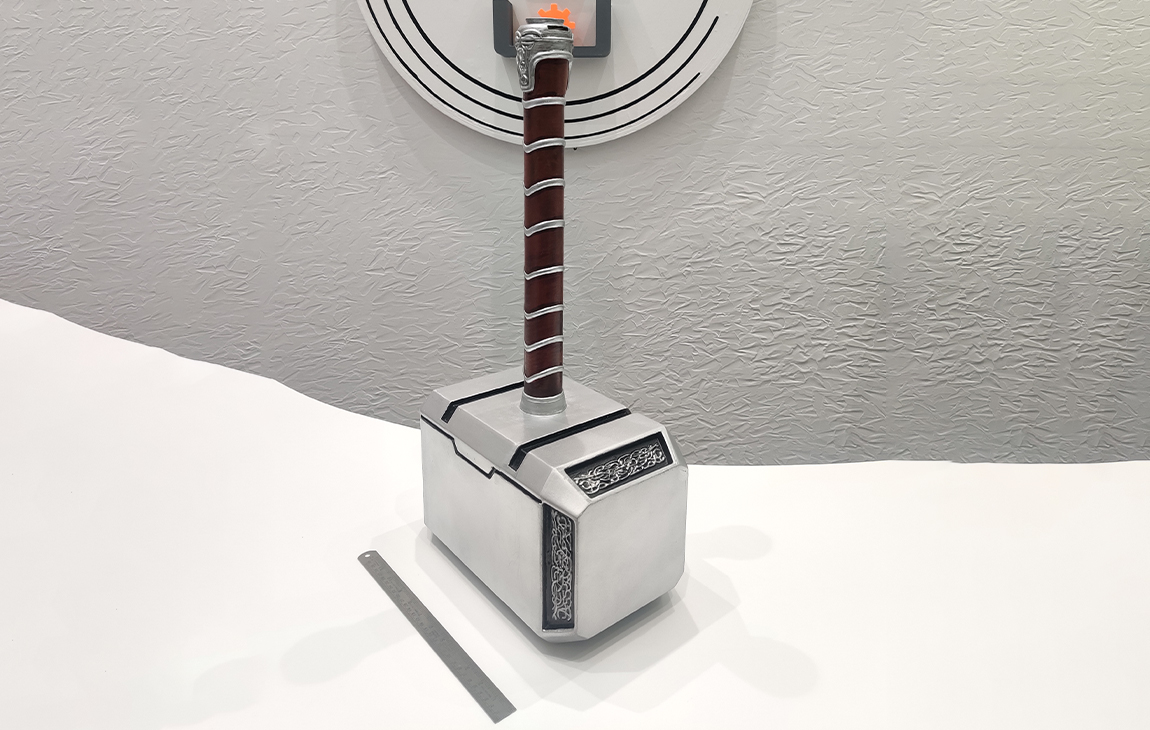
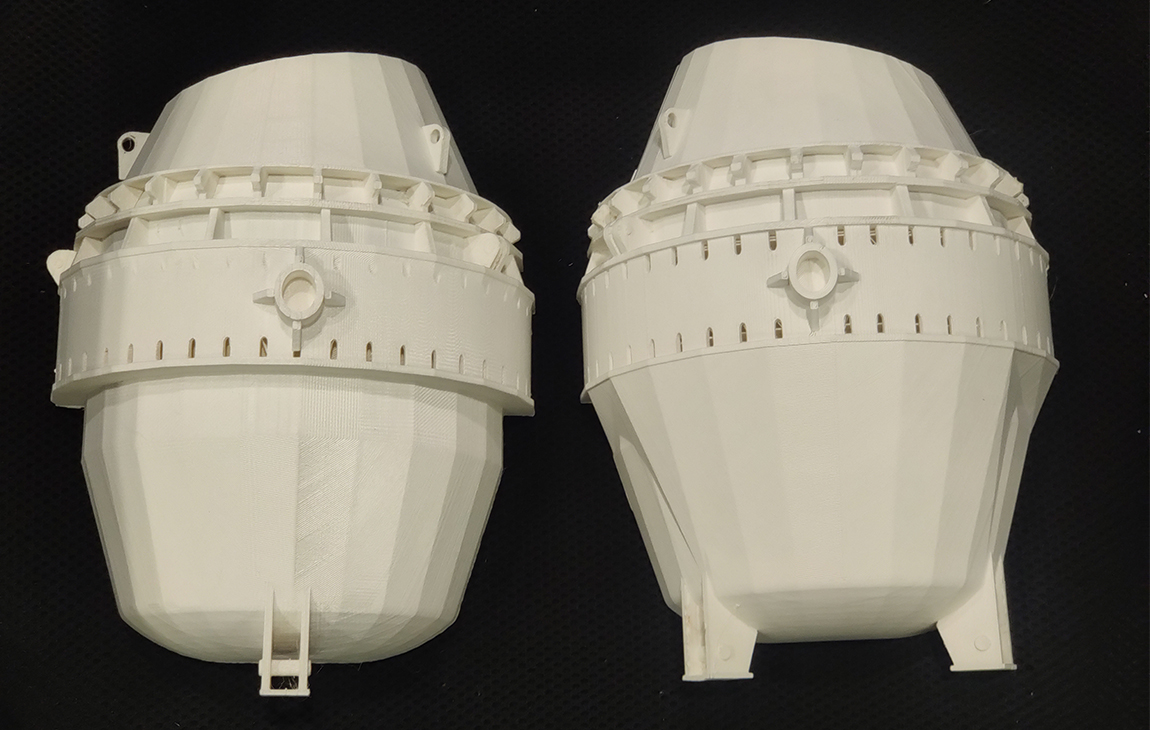
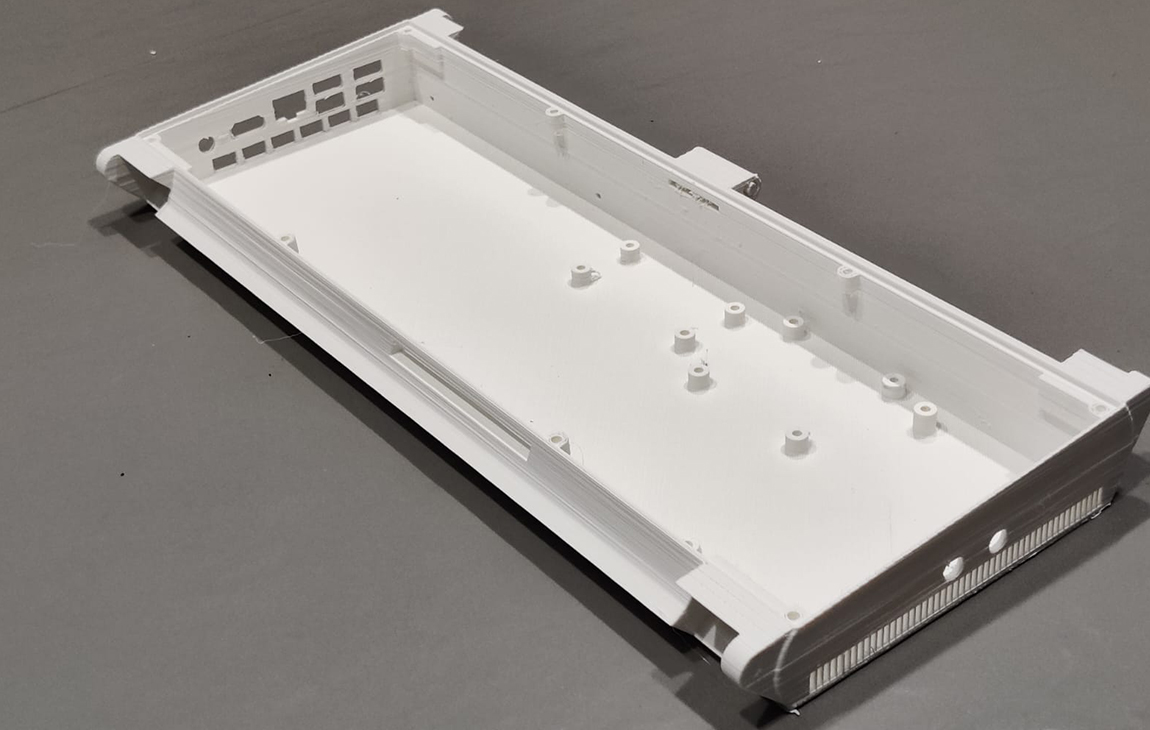
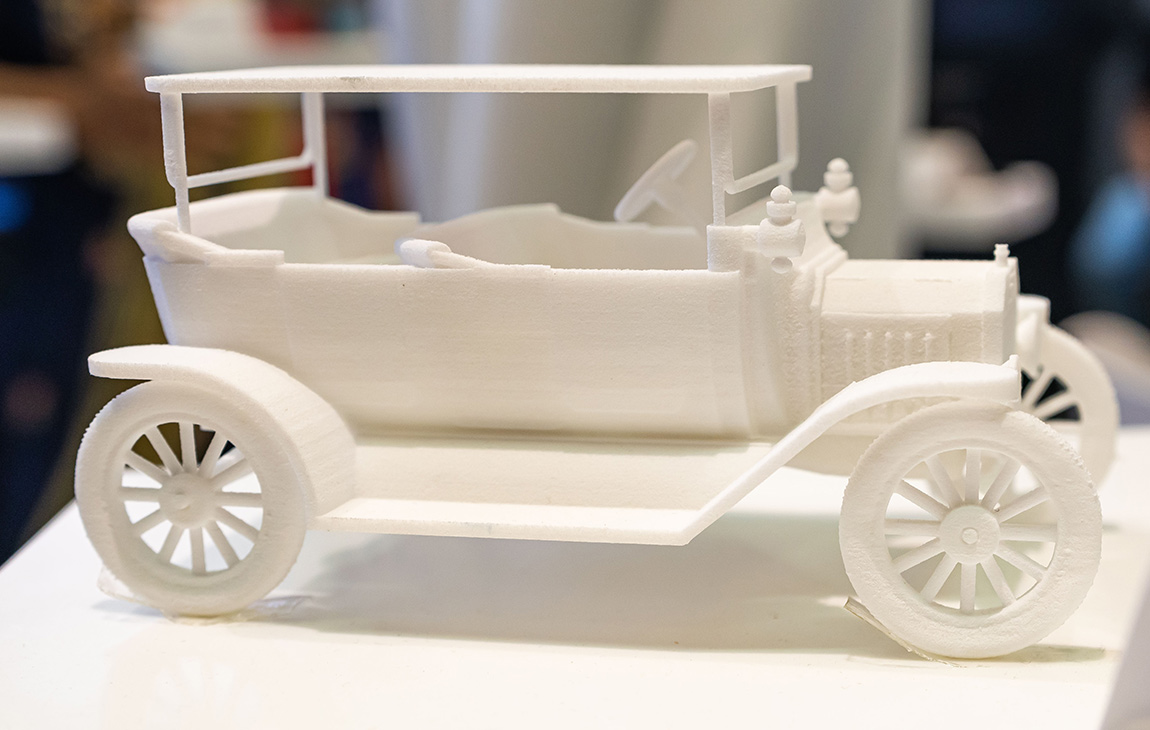
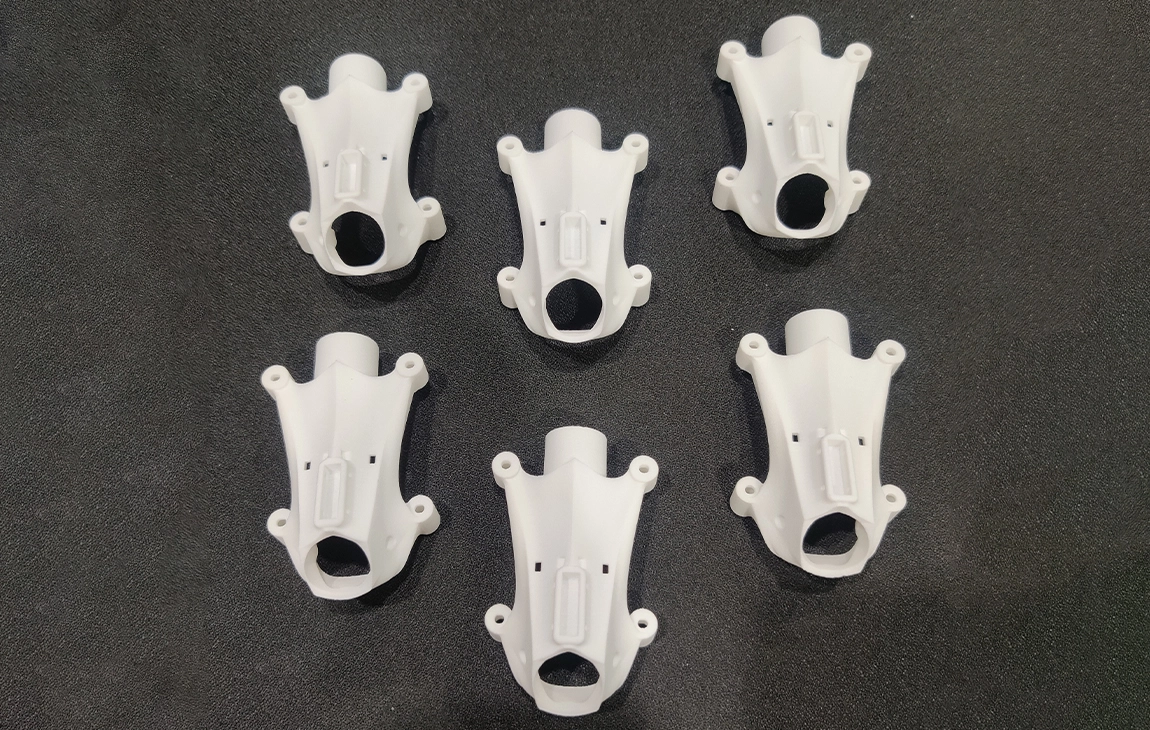
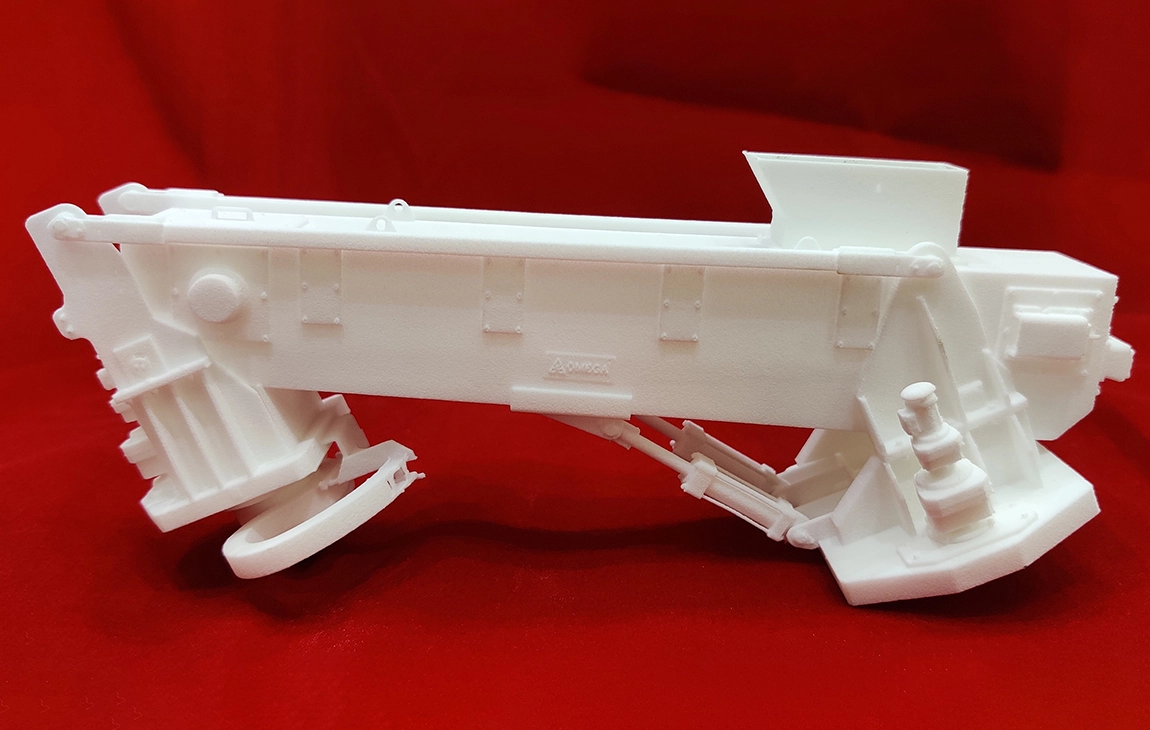
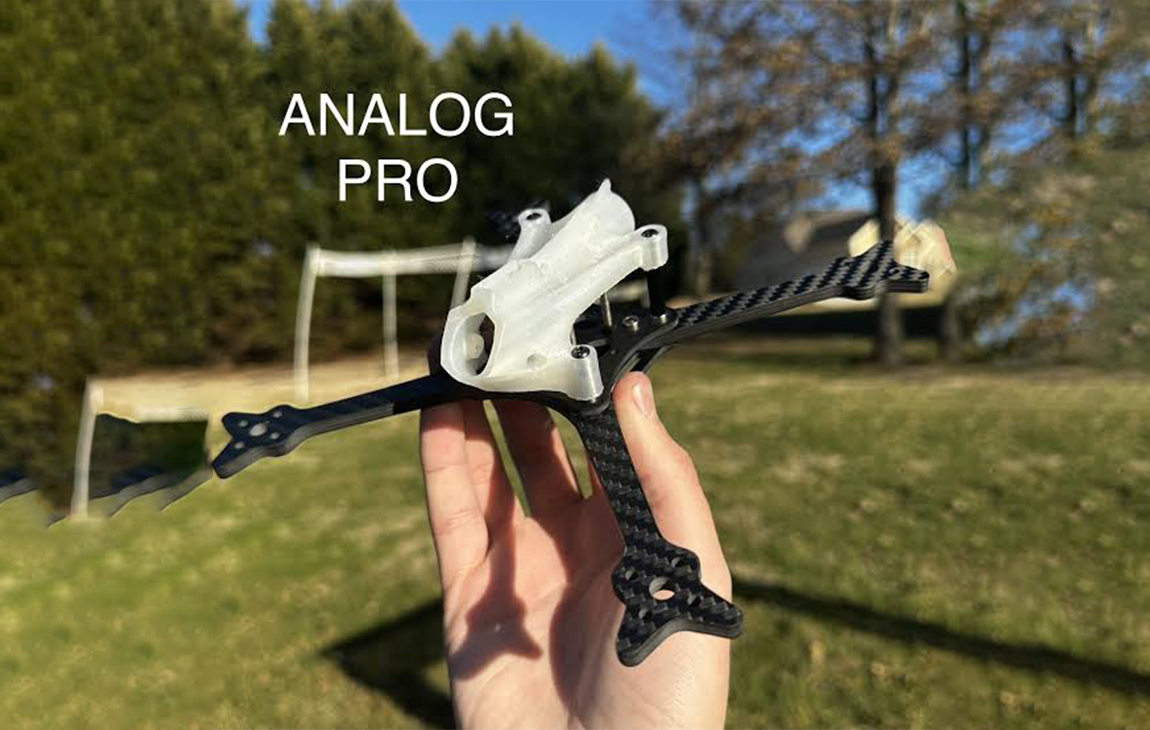
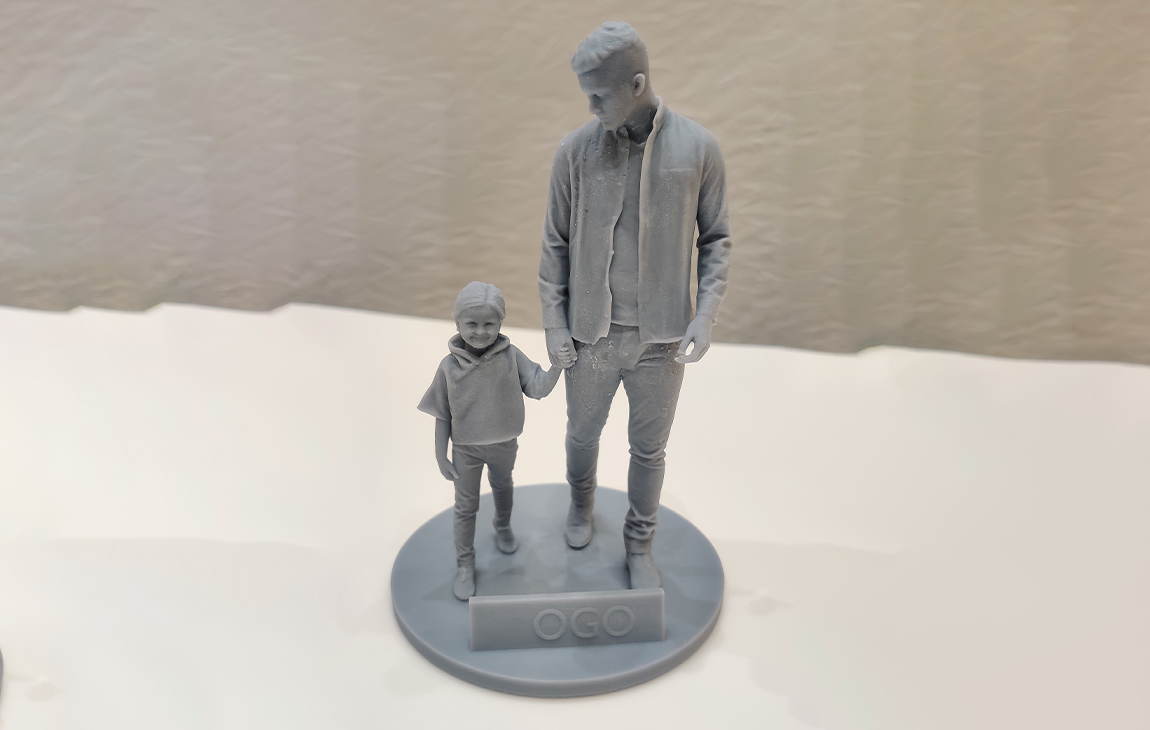
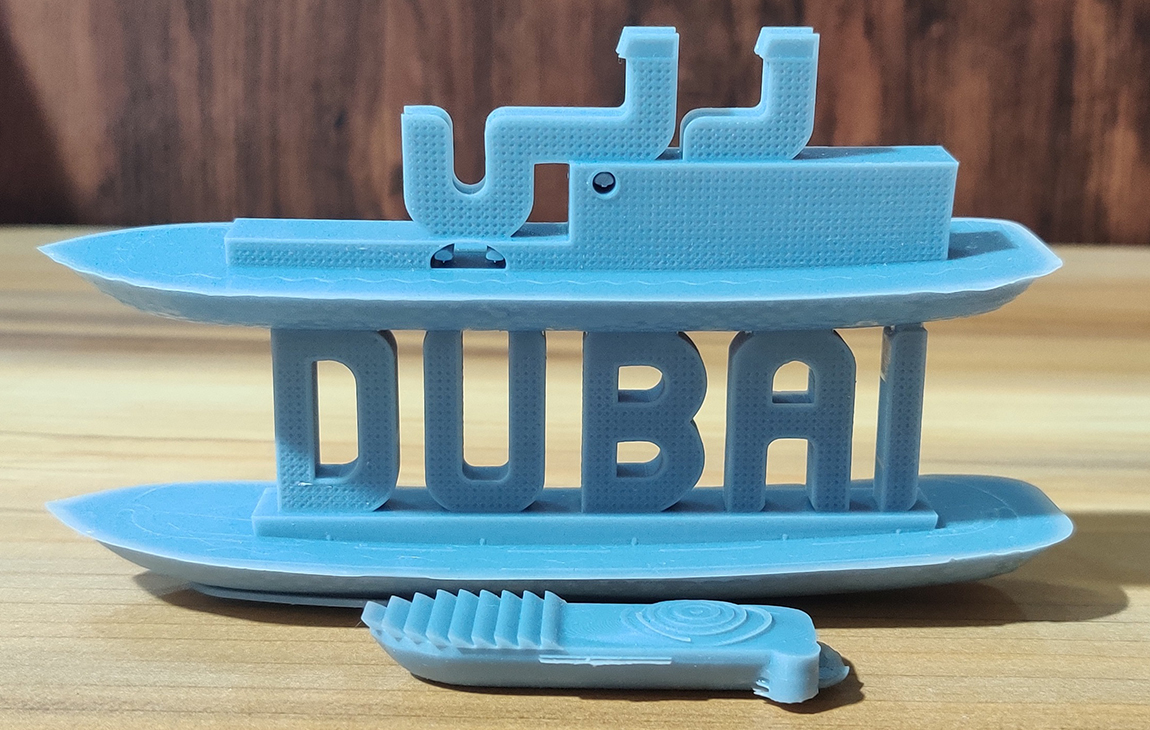
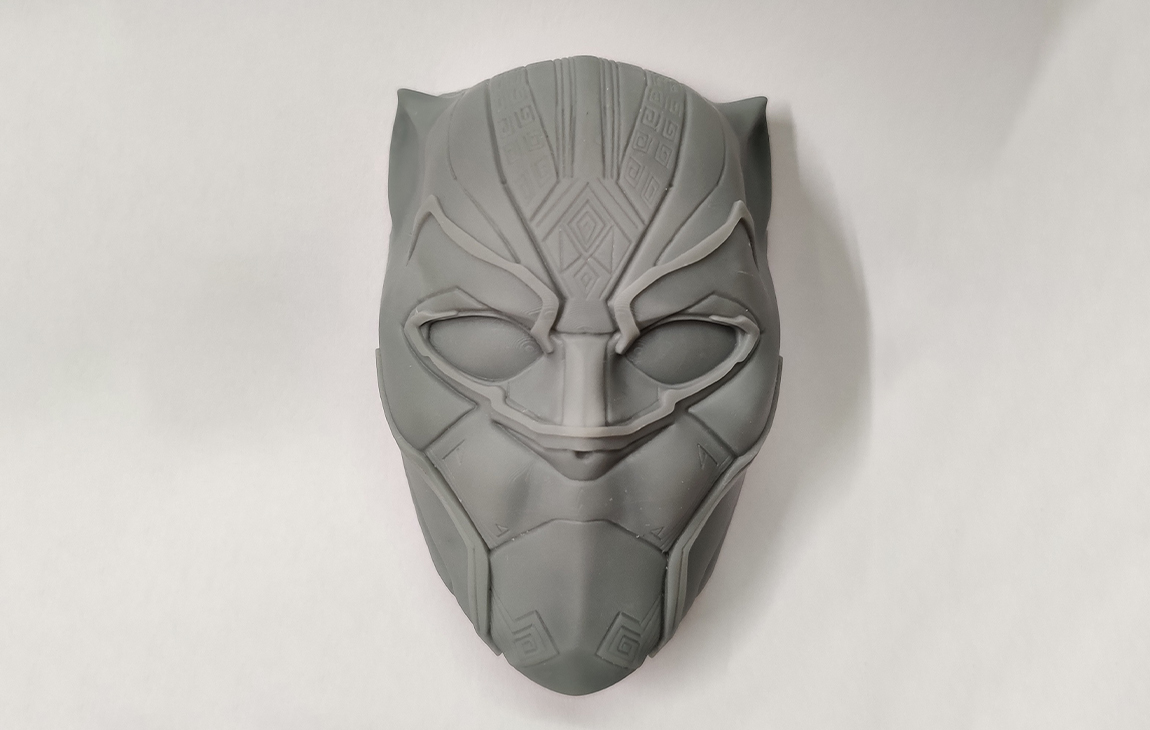
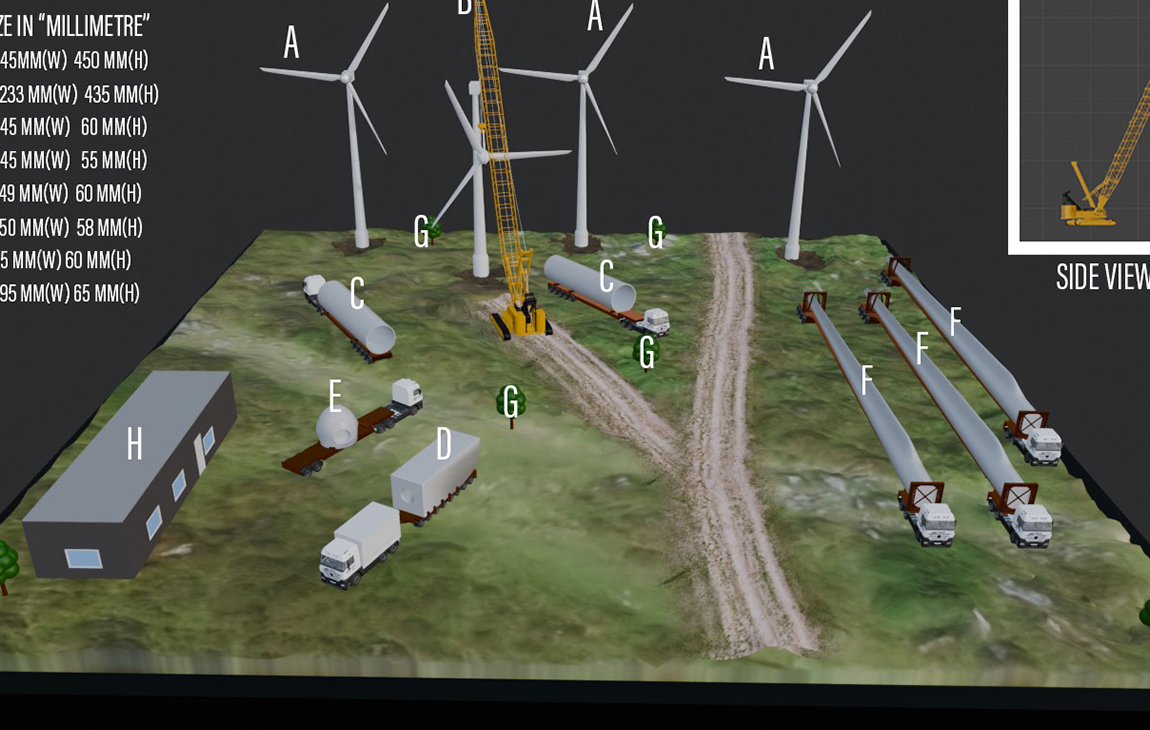
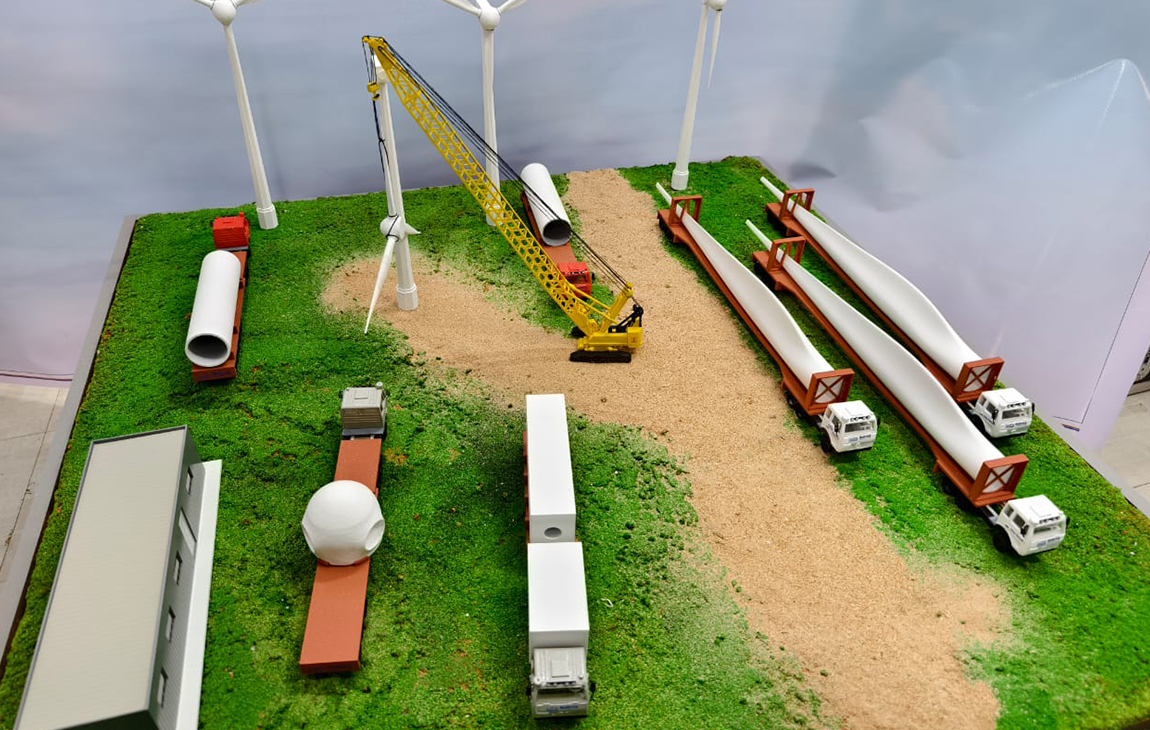
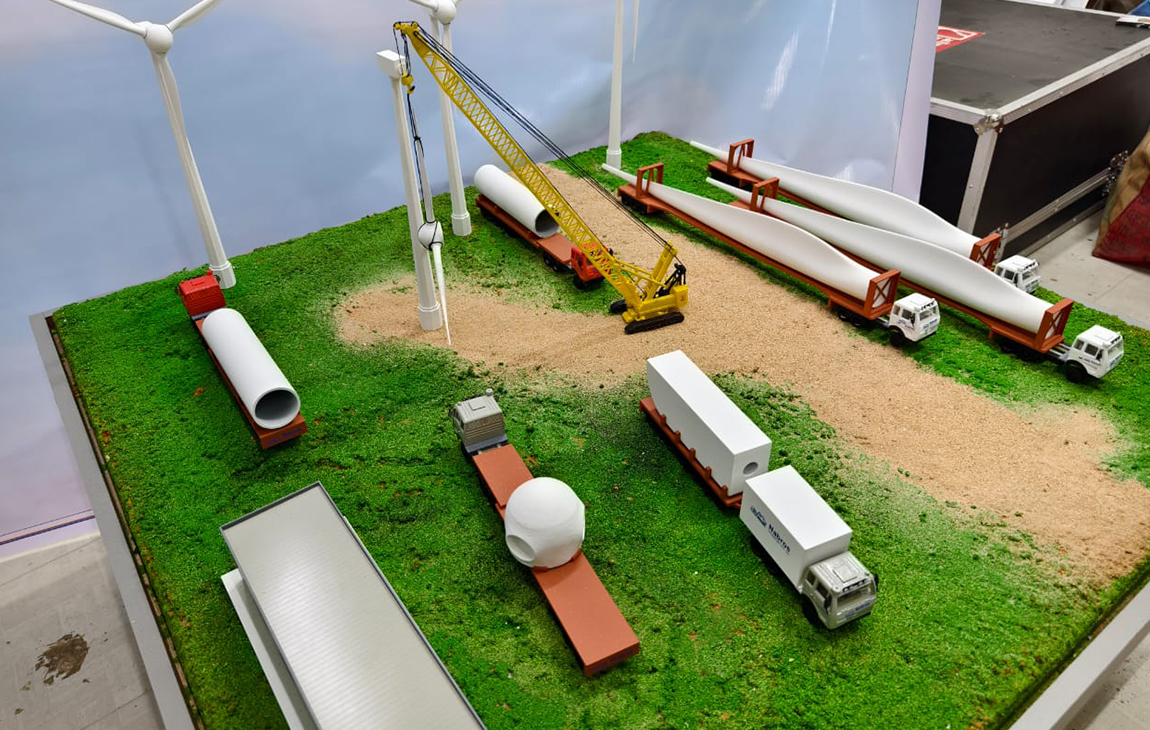
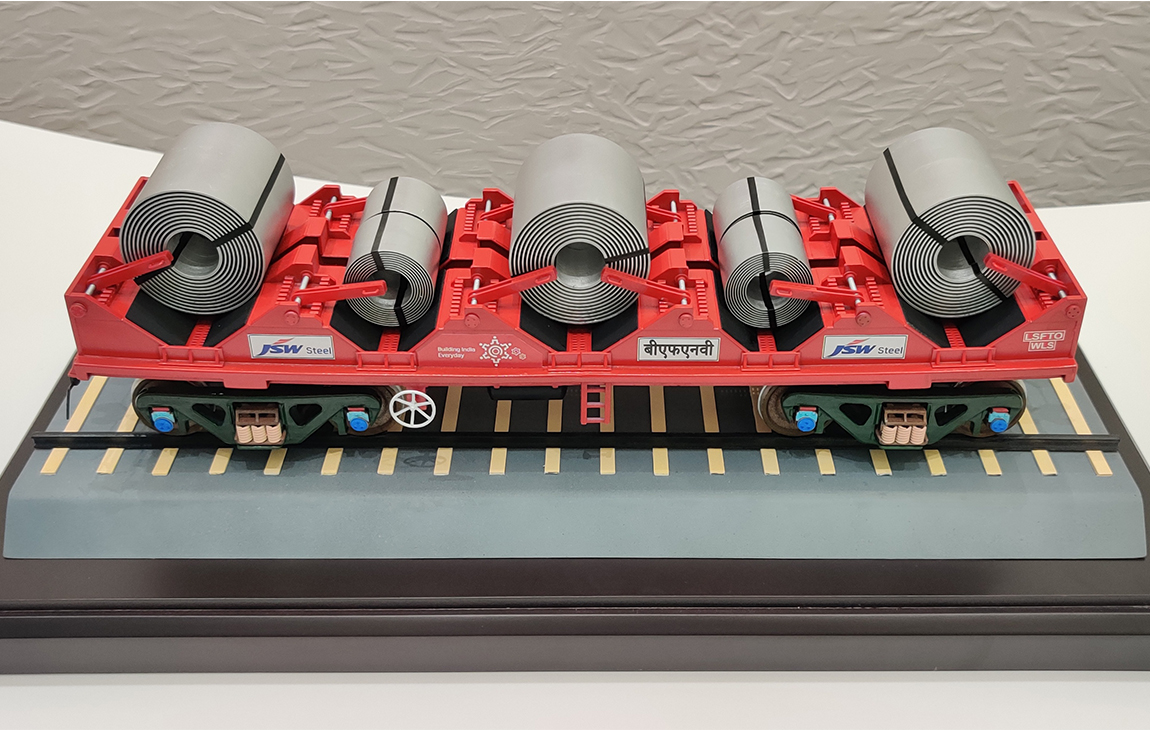
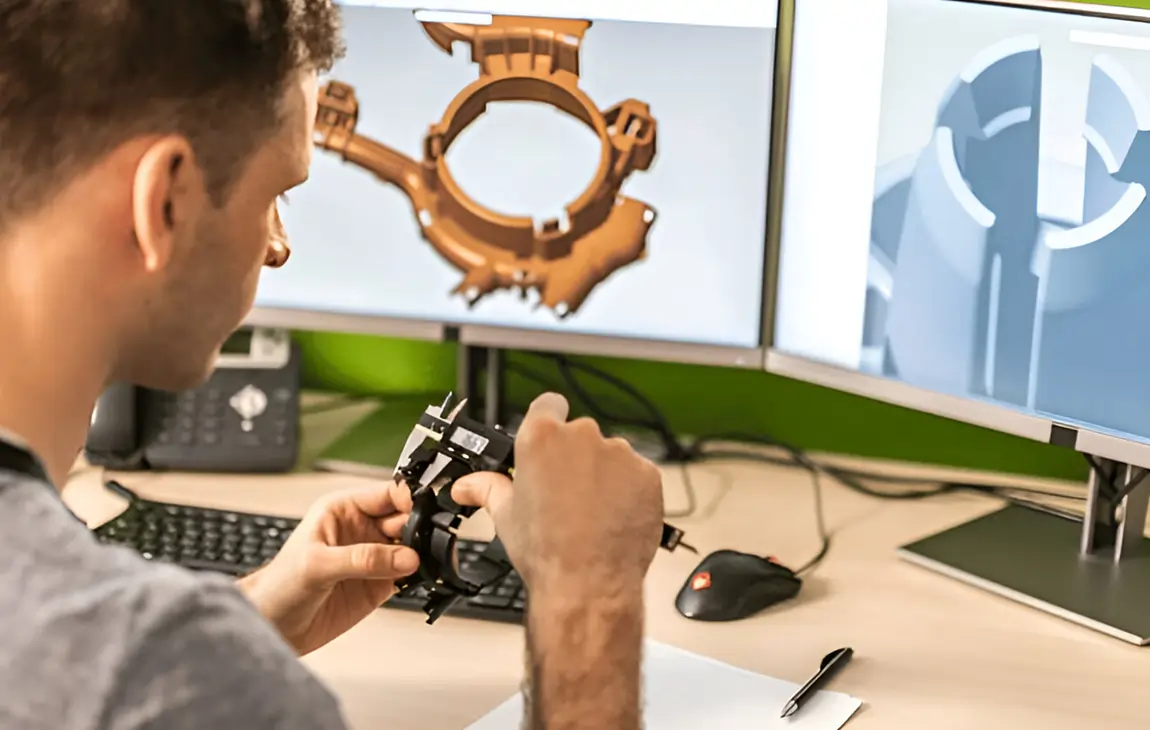
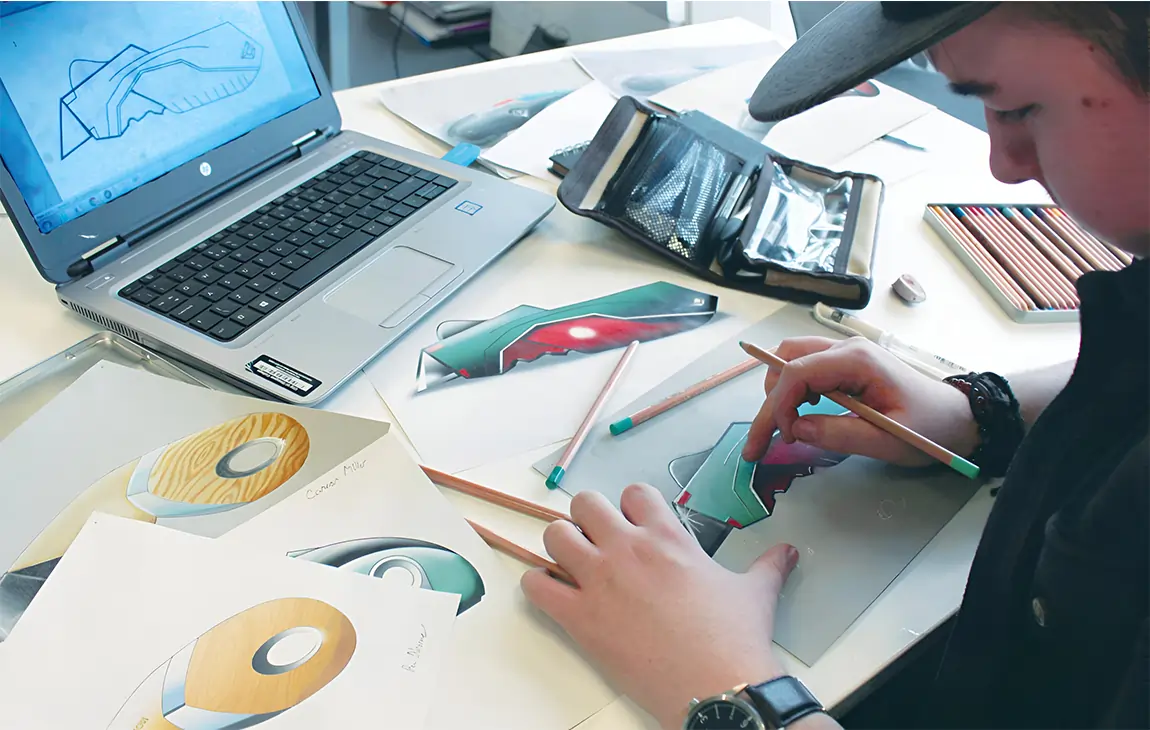
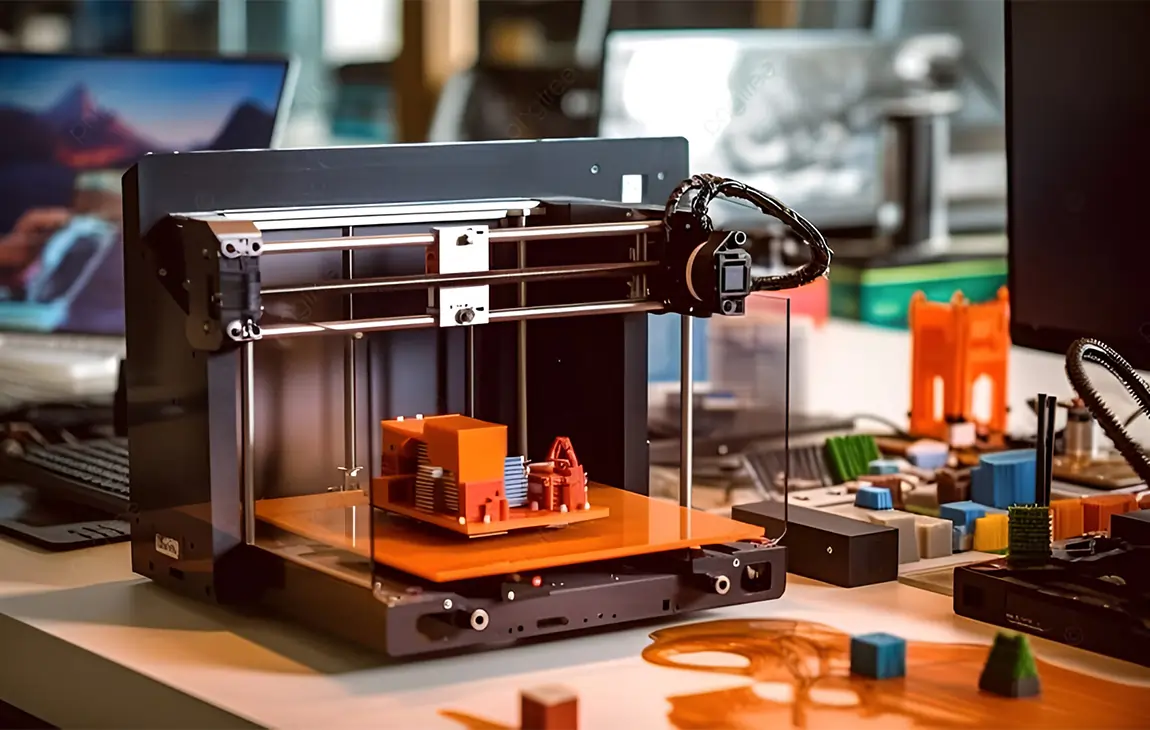
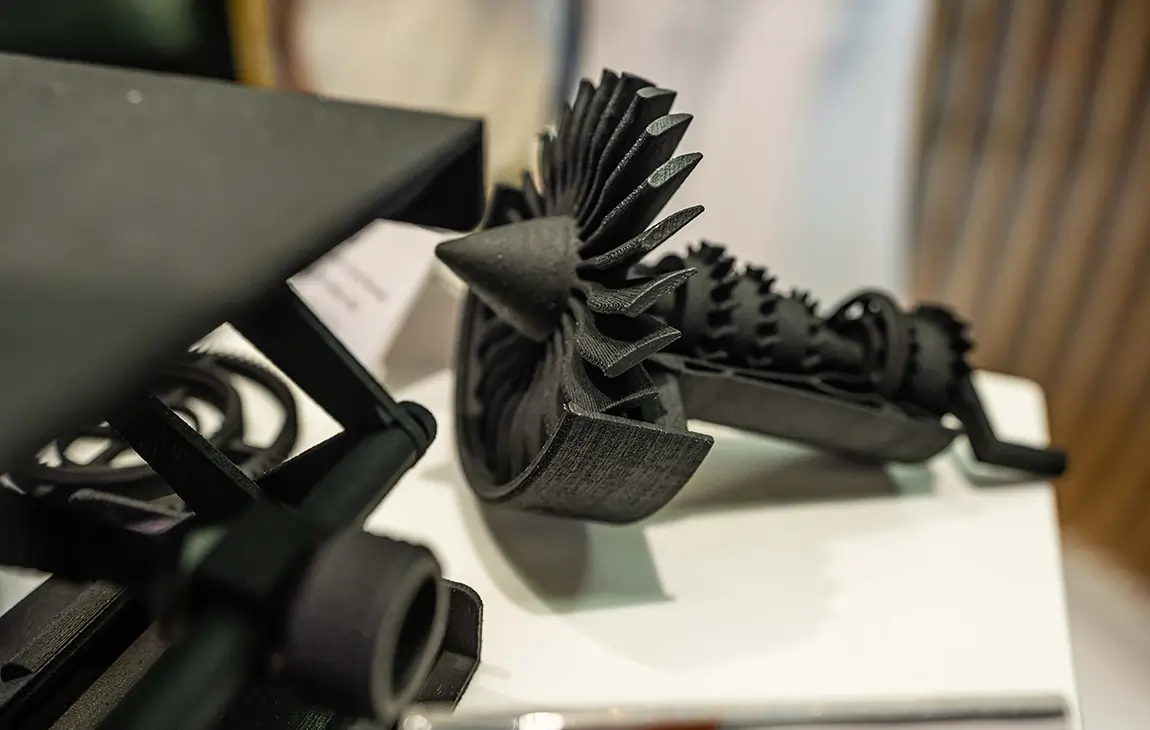
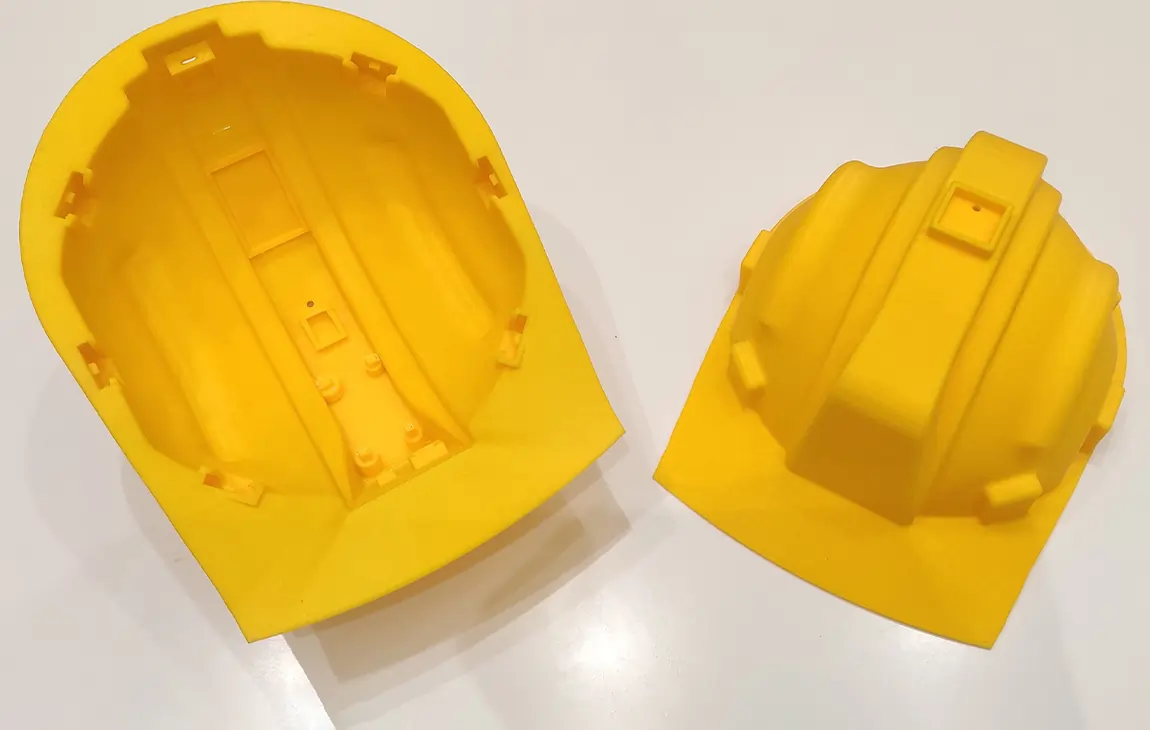
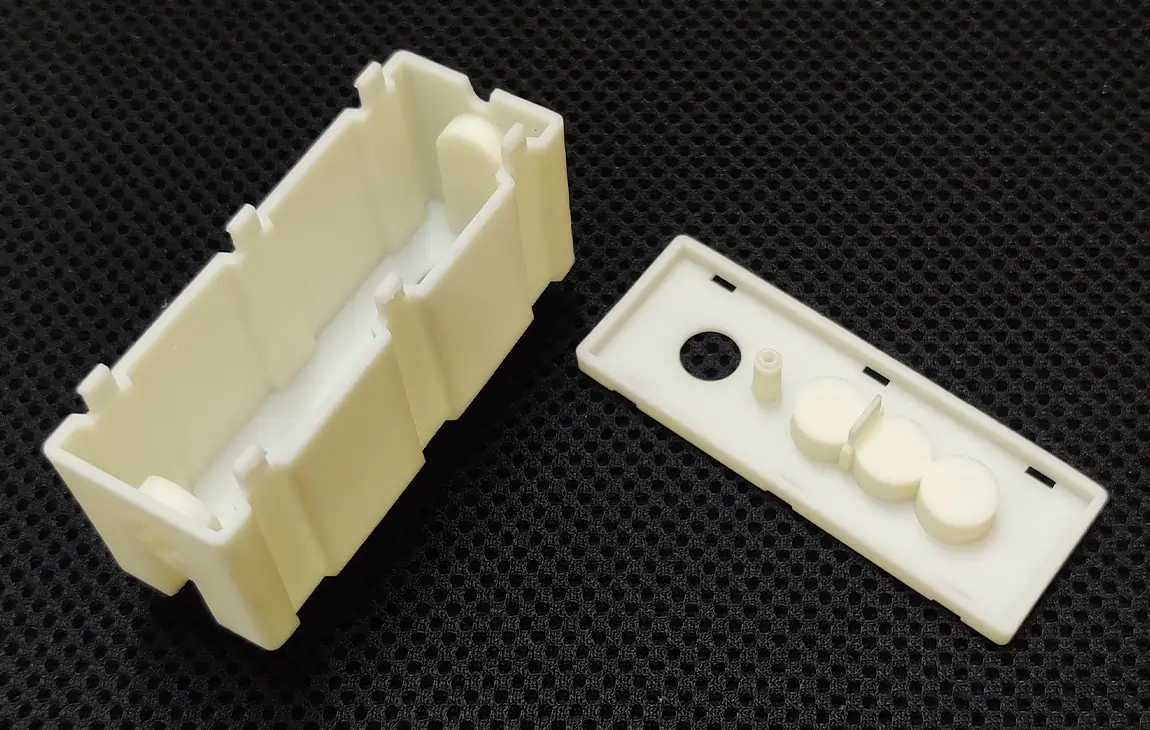
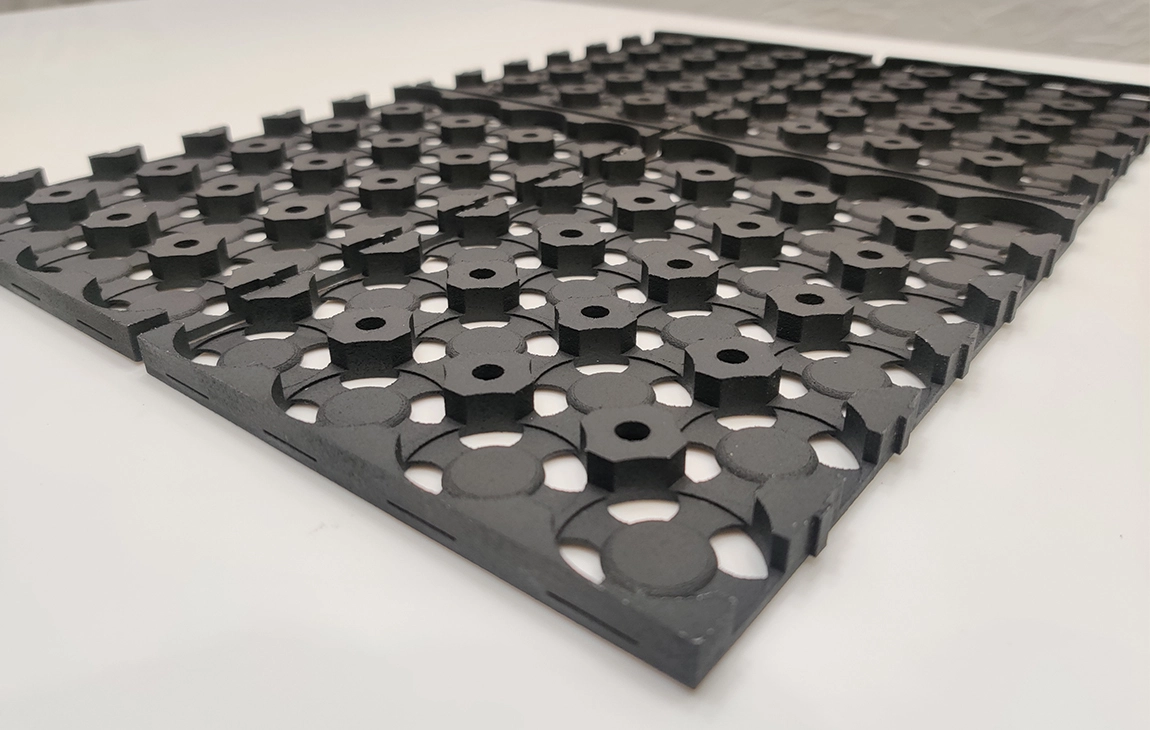
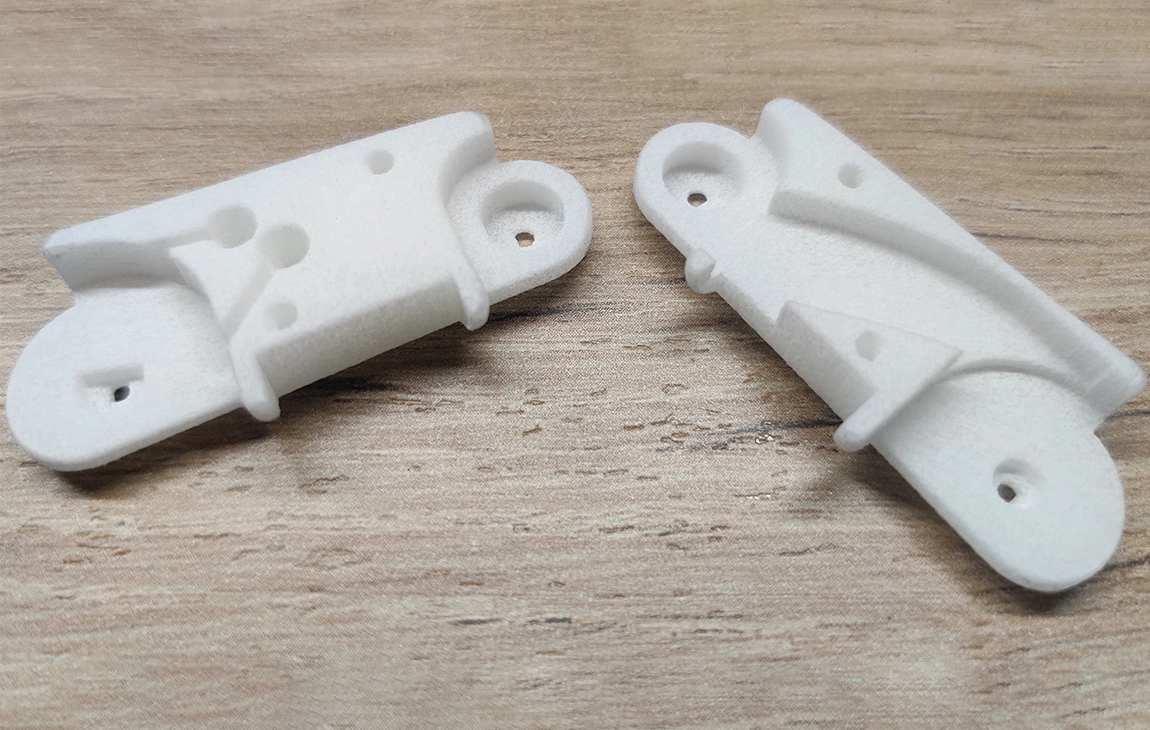
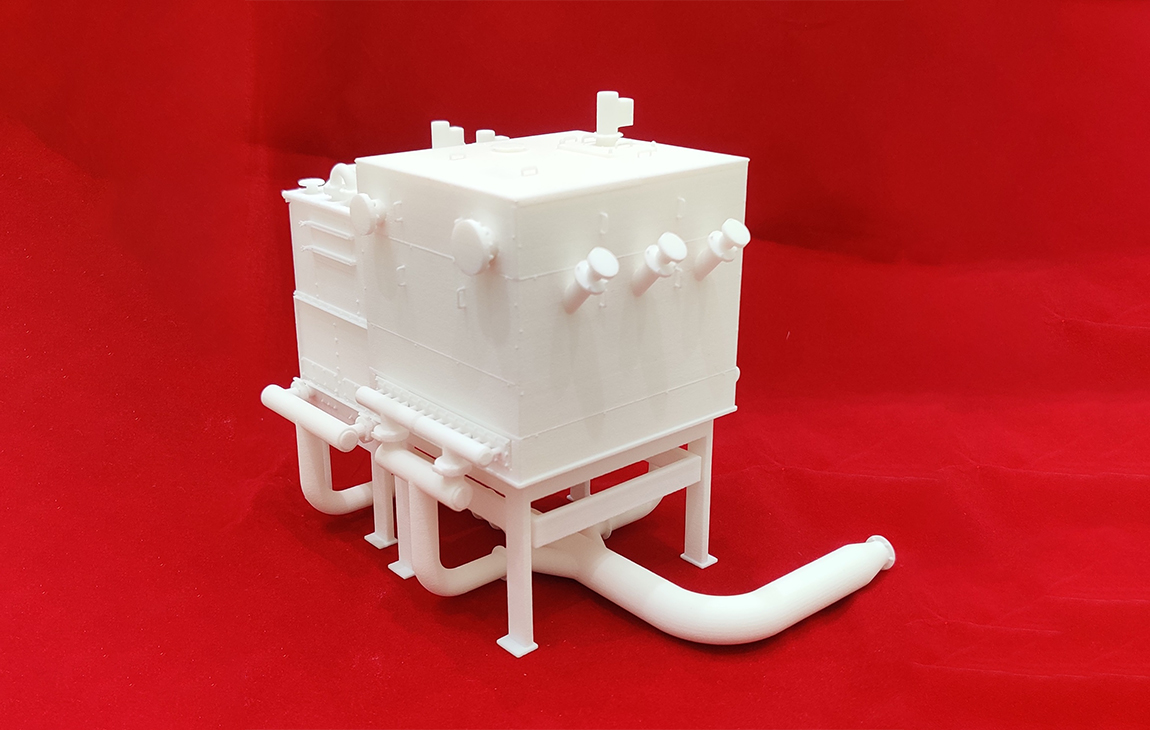
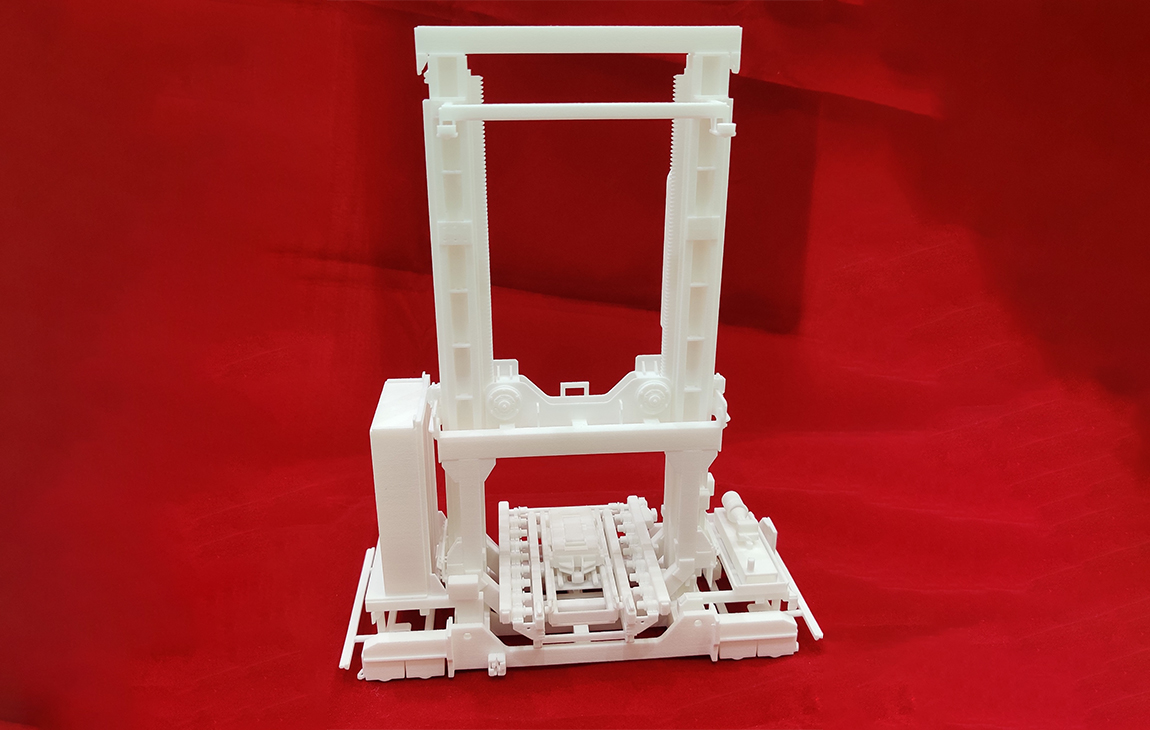
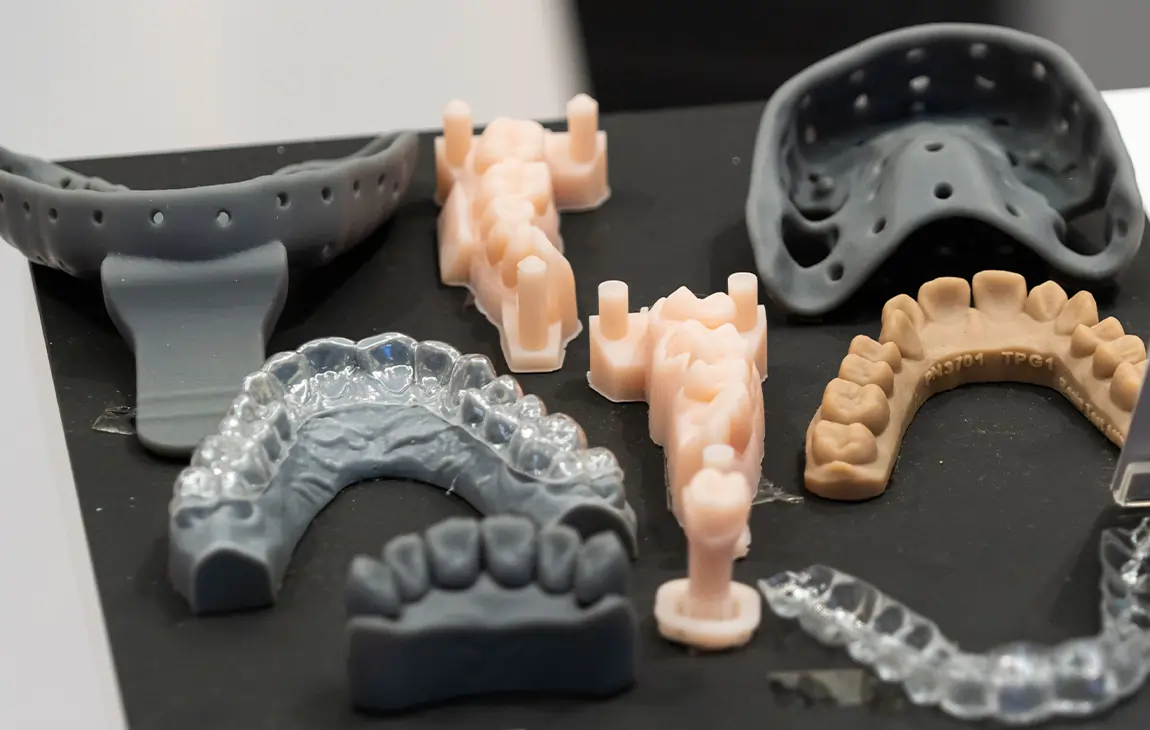
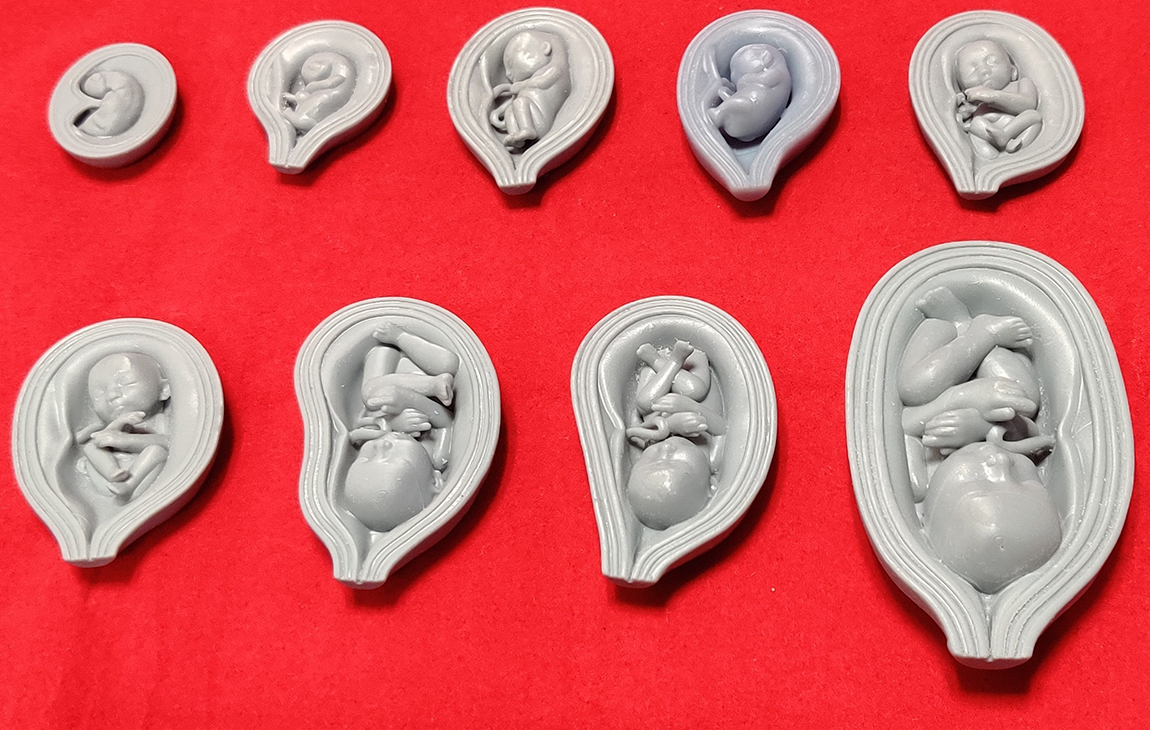
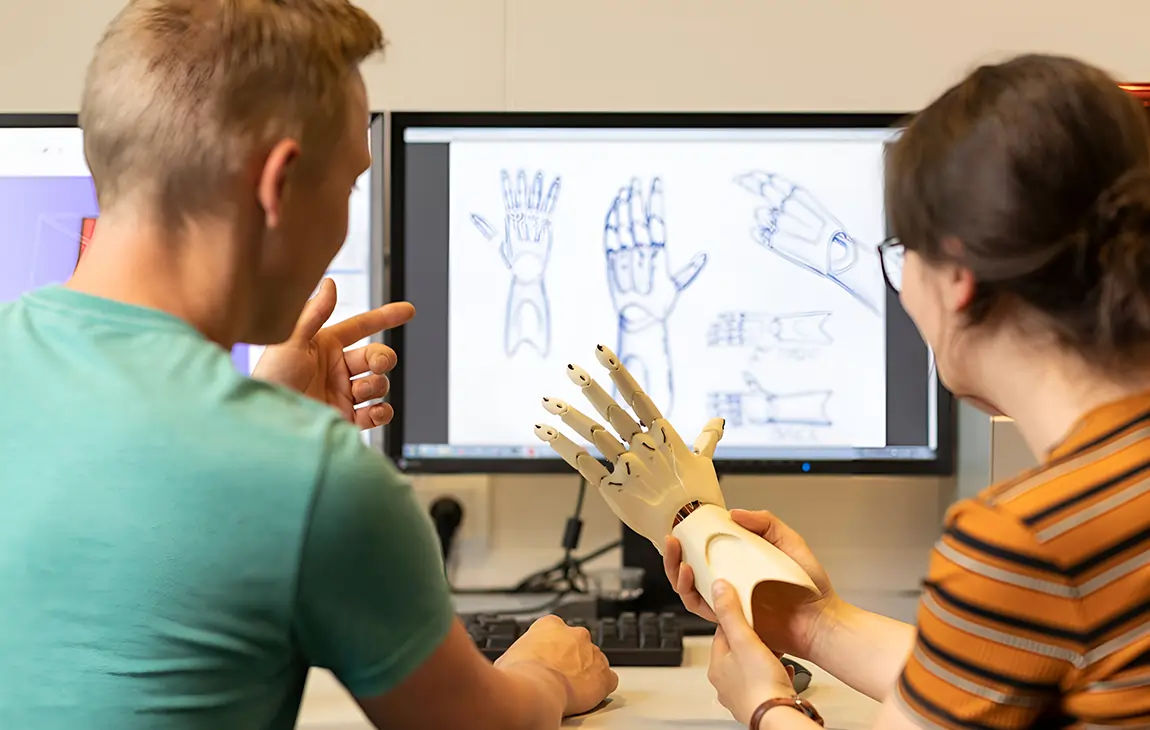
RAPID PROTOTYPING
Rapid prototyping in 3D printing is a technique that allows designers and engineers to quickly create physical models from digital designs. Using 3D printers, a prototype can be built layer by layer, often in just hours or days, allowing for fast testing, evaluation, and refinement of concepts. This method helps speed up the product development process, as it enables early detection of design flaws and facilitates improvements before moving into large-scale production. It’s a cost-effective way to experiment with and iterate on new ideas in industries like manufacturing, product design, and engineering.
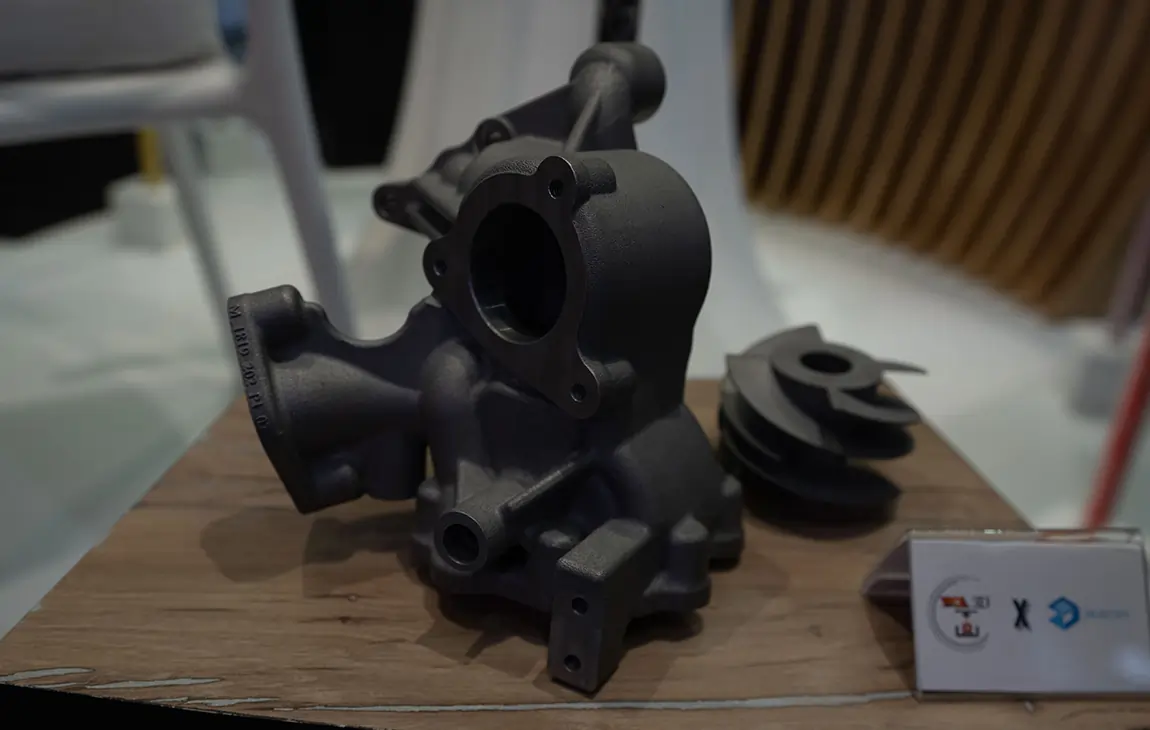
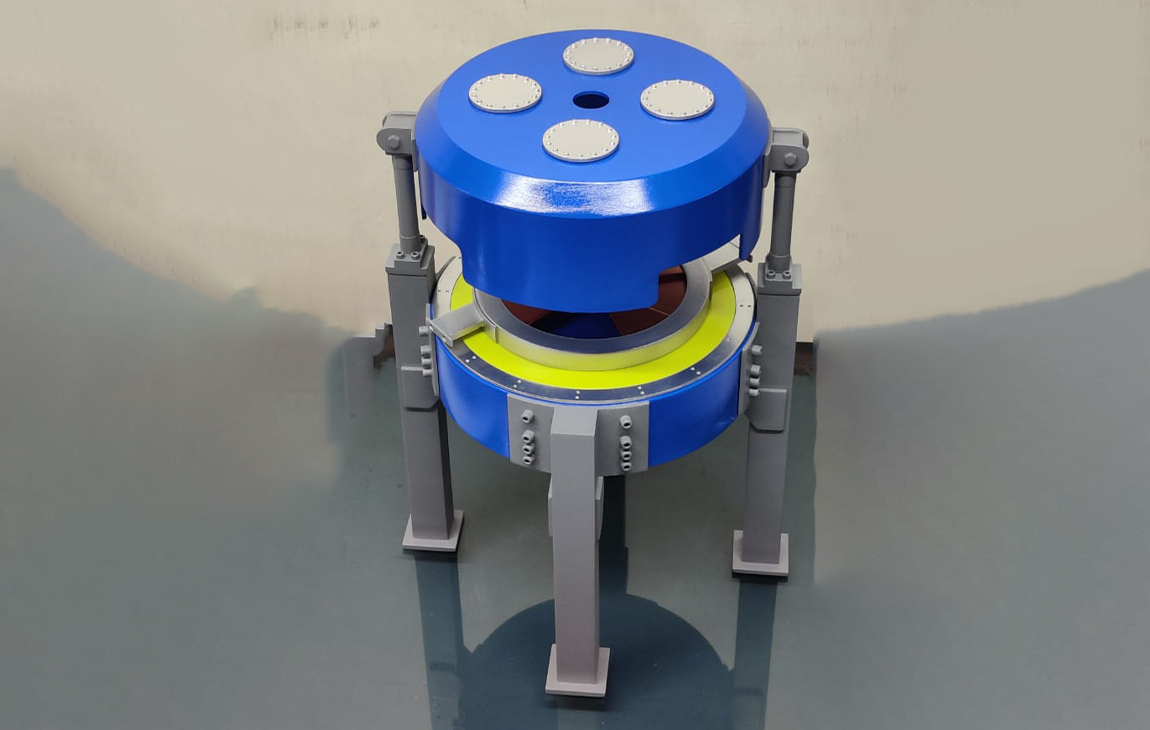
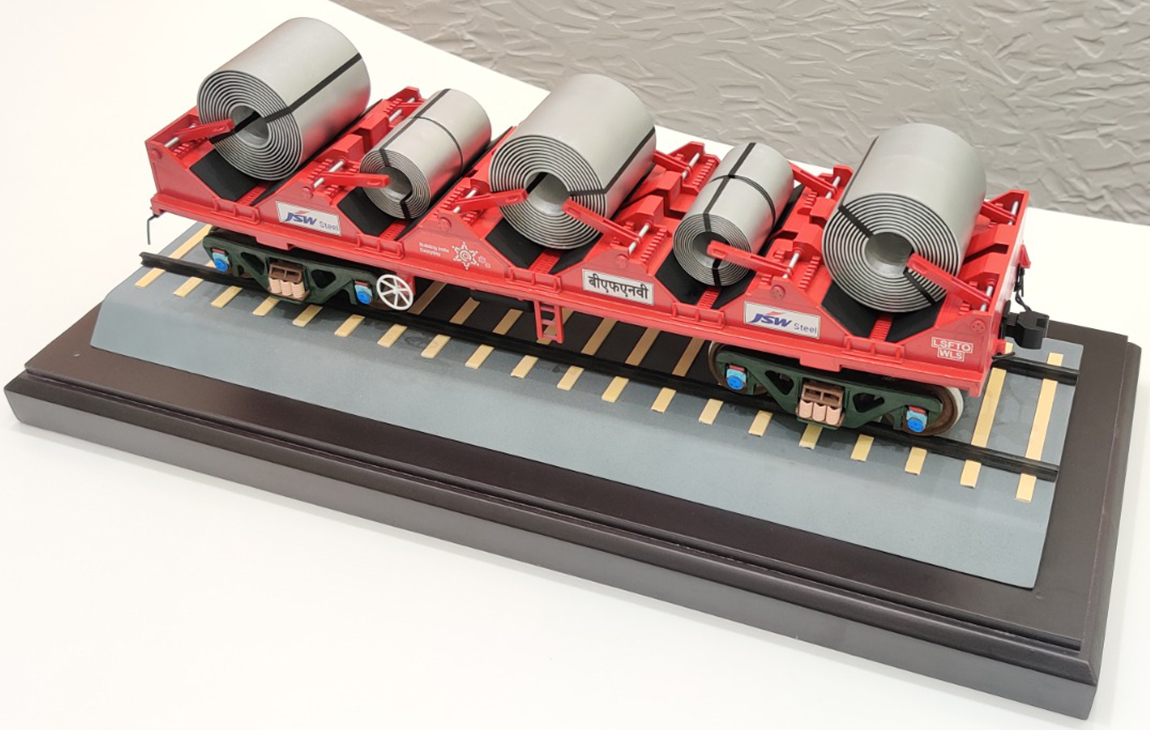
Our Creations
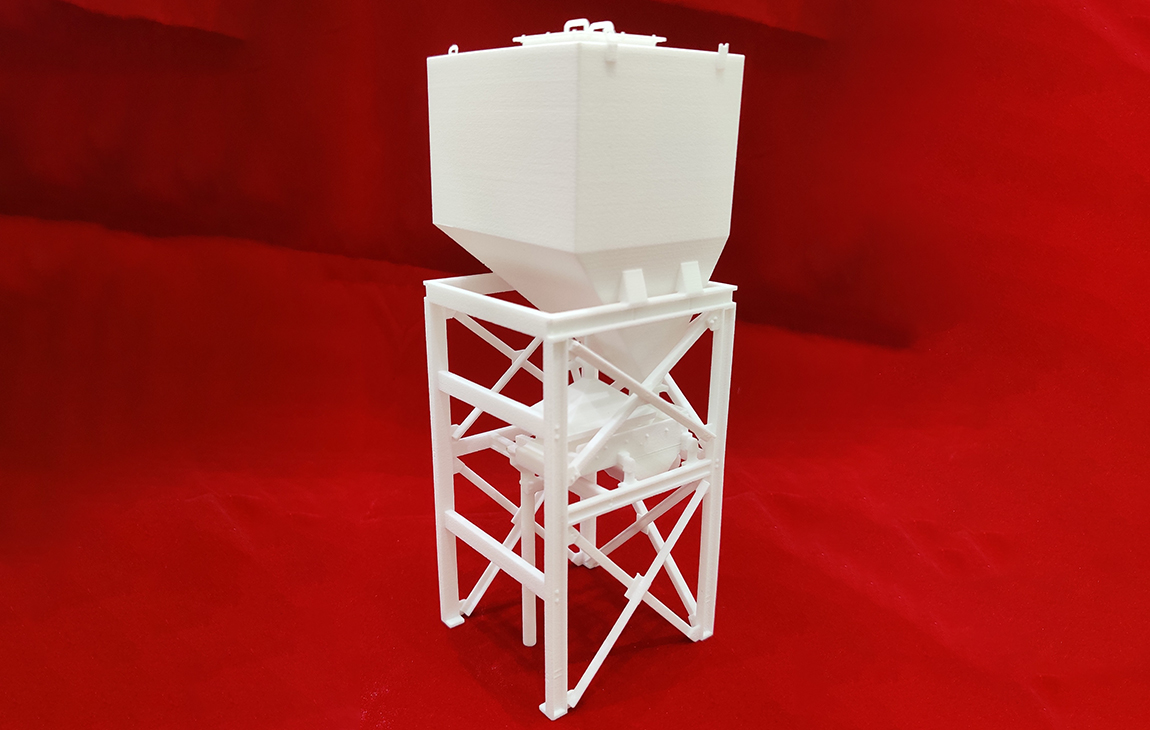
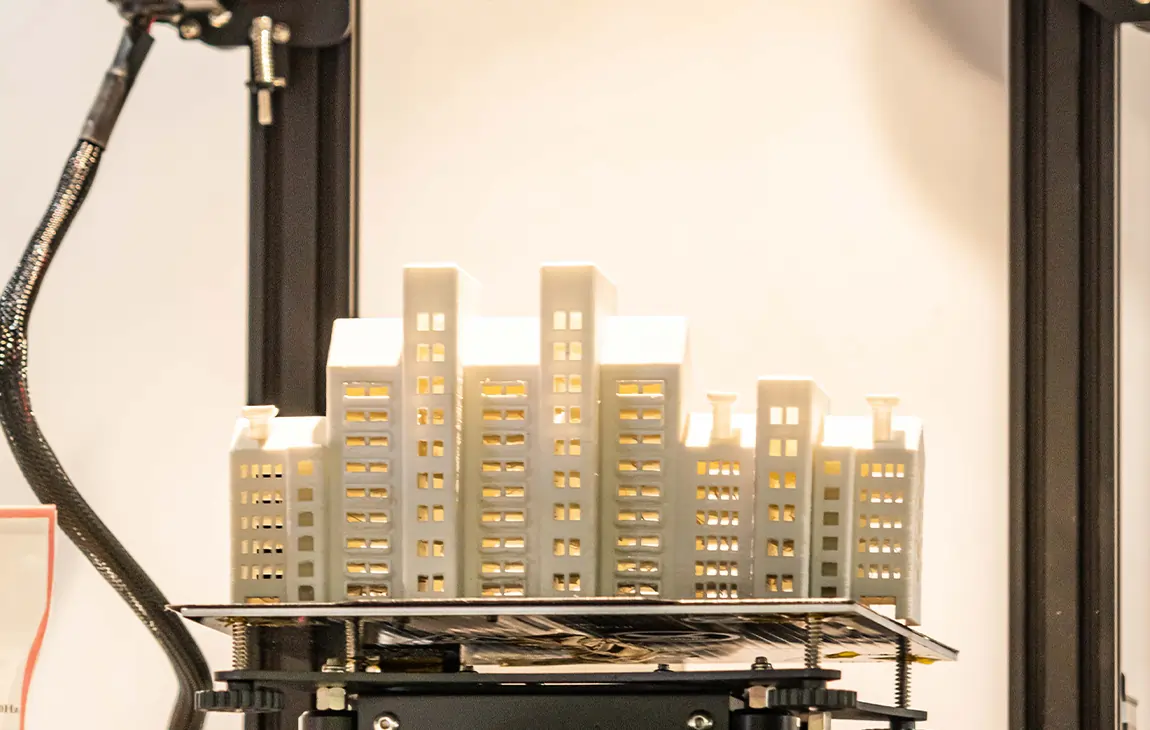
FDM 3D PRINTING
FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling) 3D printing is a popular technique where a 3D printer melts and extrudes thermoplastic material, layer by layer, to build up a physical object. The printer follows a precise digital design, and as each layer cools and solidifies, it forms part of the final object. FDM is widely used because it’s affordable, versatile, and suitable for creating prototypes, functional parts, and models. Common materials used in FDM printing include PLA, ABS, TPU and PETG, which are known for their durability and ease of use.
This method is especially popular in industries like manufacturing, education, and engineering for rapid prototyping and production.
Our Creations
SLS 3D PRINTING
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) 3D printing is an advanced technique where a laser is used to selectively melt and fuse powdered material, usually plastic, metal, or ceramic, into solid layers to create a 3D object. The laser scans and sinters (melts) the powder according to a digital design, and each layer bonds to the one below it. SLS is known for producing highly durable, complex, and detailed parts, often used for functional prototypes or small-batch production.
Unlike other methods, SLS doesn’t require support structures, as the surrounding powder acts as support during the printing process. It’s widely used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare for creating parts with intricate geometries and high strength.
Our Creations
SLA 3D PRINTING
SLA (Stereolithography) 3D printing is a technique that uses a laser to cure liquid resin layer by layer to create a solid 3D object. The resin is contained in a vat, and the laser selectively hardens the resin based on a digital design, building the object from the bottom up. SLA is known for its high precision and ability to produce very detailed, smooth, and accurate parts, making it ideal for applications where fine detail is crucial, such as in jewelry, dentistry, or high-end prototypes.
It offers superior surface finishes compared to other 3D printing methods, but the process can be slower and typically requires post-processing to clean and cure the printed parts.
Our Creations
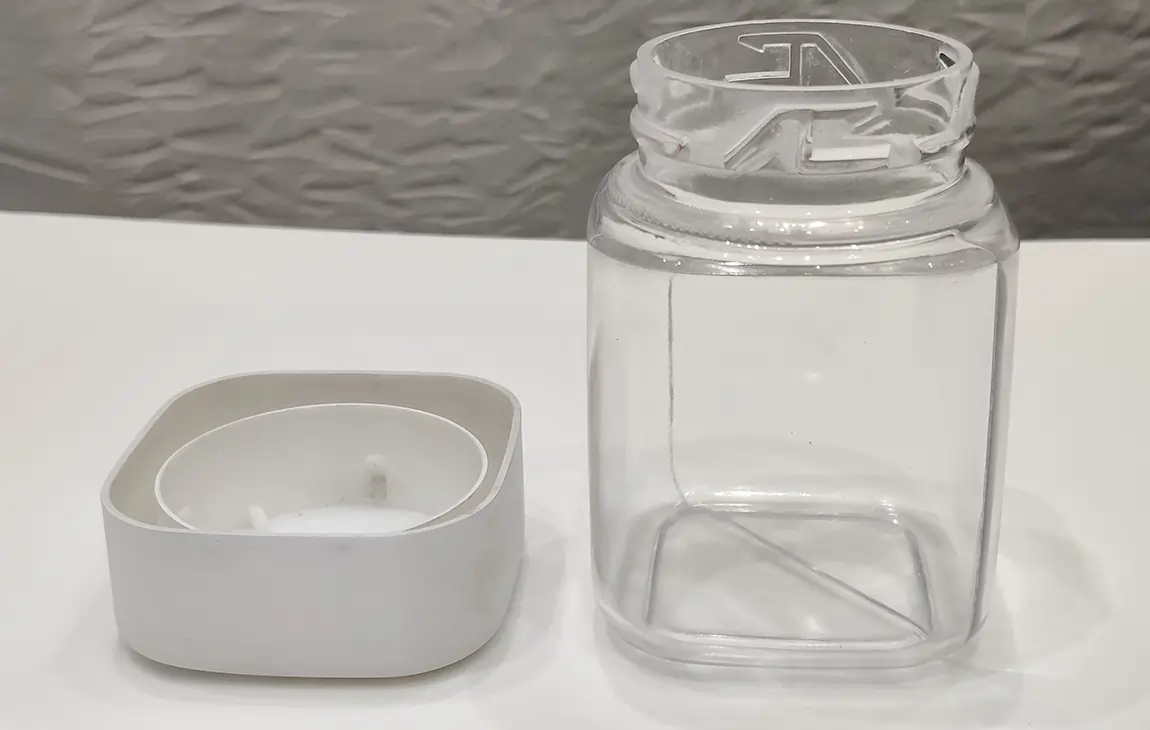
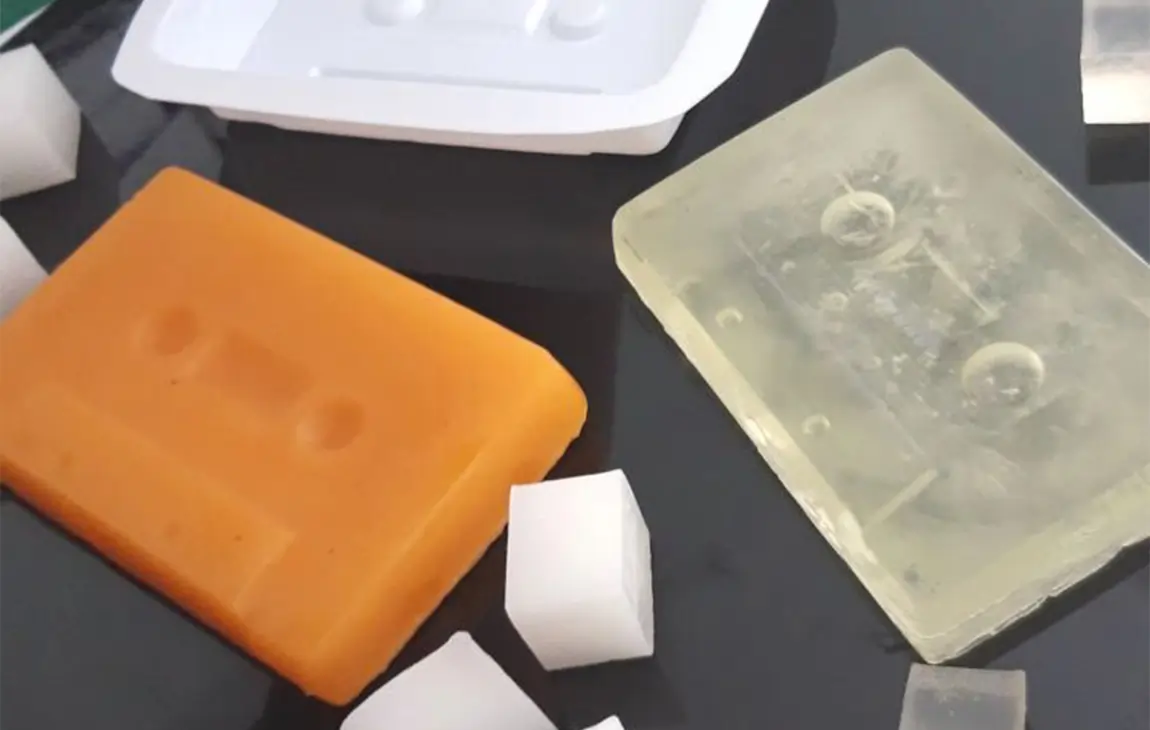
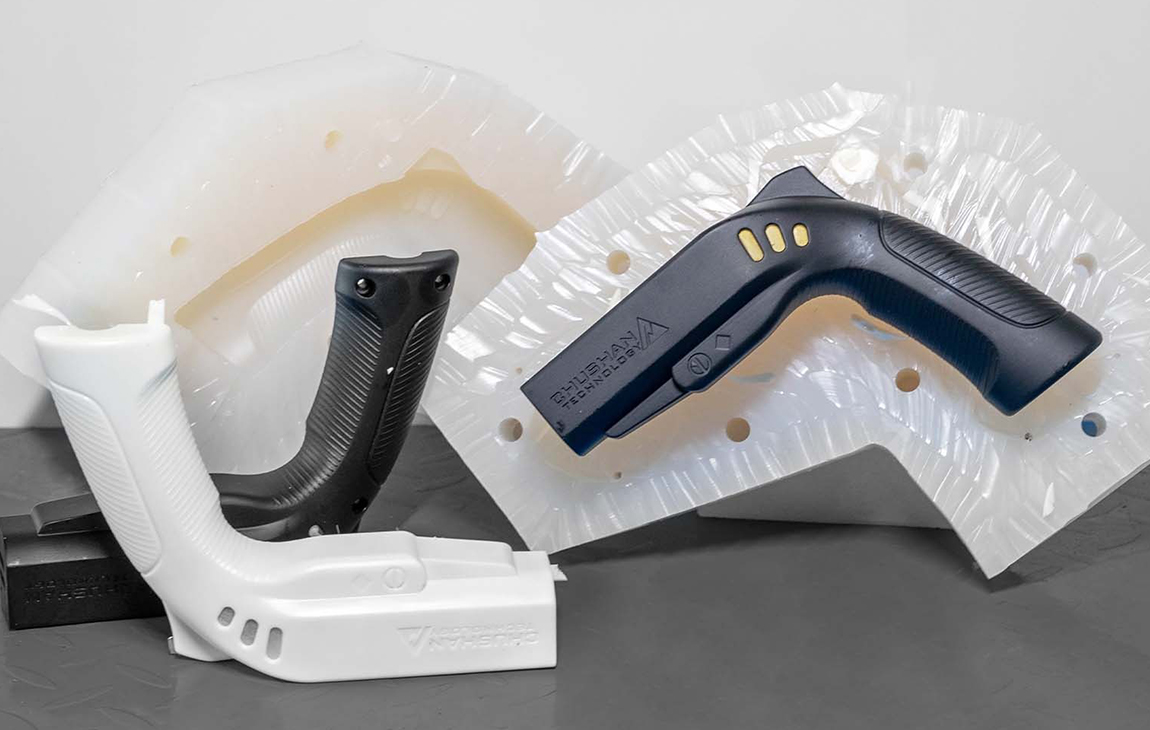
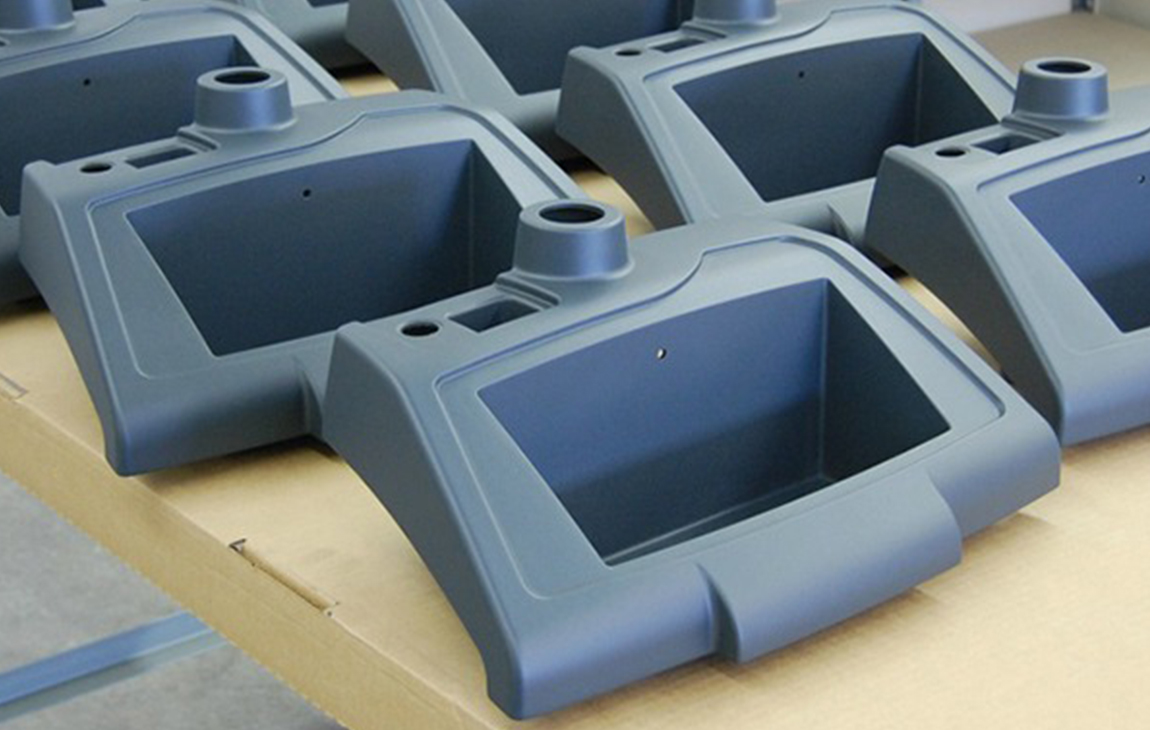
VACUUM CASTING
Vacuum casting is a casting process for elastomers using a vacuum to draw the liquid material into the mold. This process is used when air entrapment is a problem, there are intricate details or undercuts, or if the material is fiber or wire reinforced.
The process starts by placing a two piece silicone mold in a vacuum chamber. The raw material is mixed, degassed and then poured into the mold. The vacuum is then released and the mold removed from the chamber. Finally, the casting is cured in an oven and the mold removed to release the completed casting.
Get high-volume of parts fabricated to the highest standards at industry-leading turnaround time. Ideal for prototypes, engineering testing, concept proofing & display demos.
Our Creations
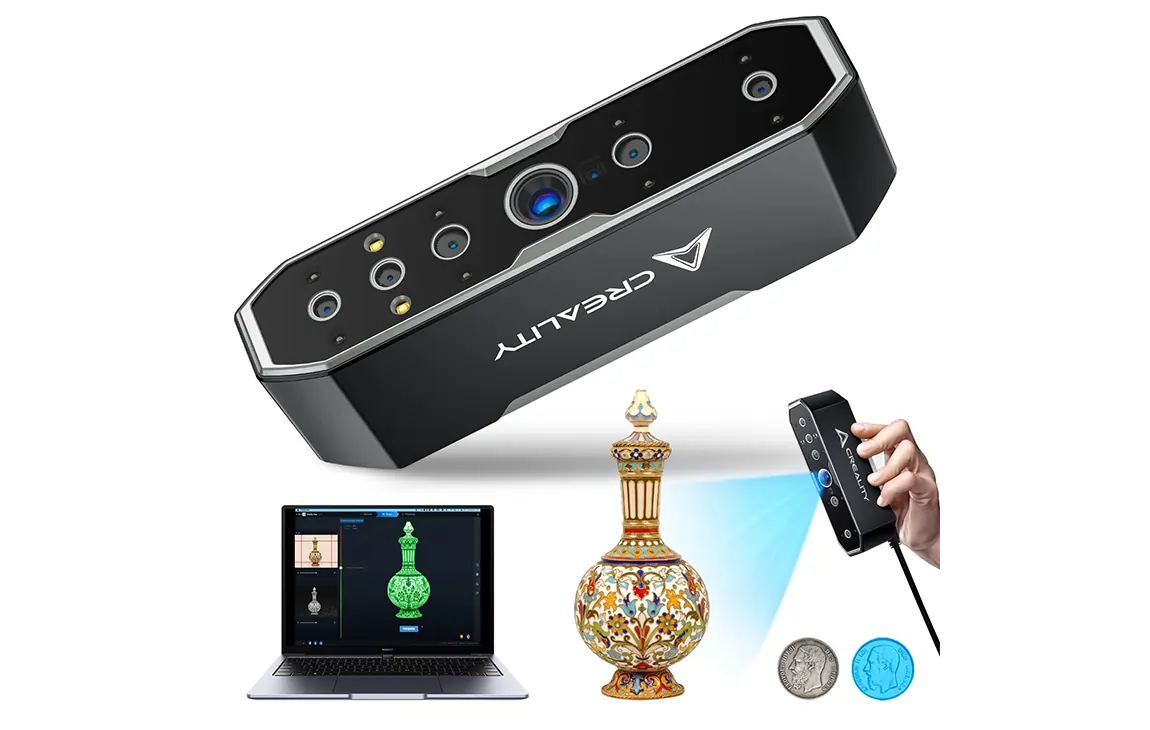
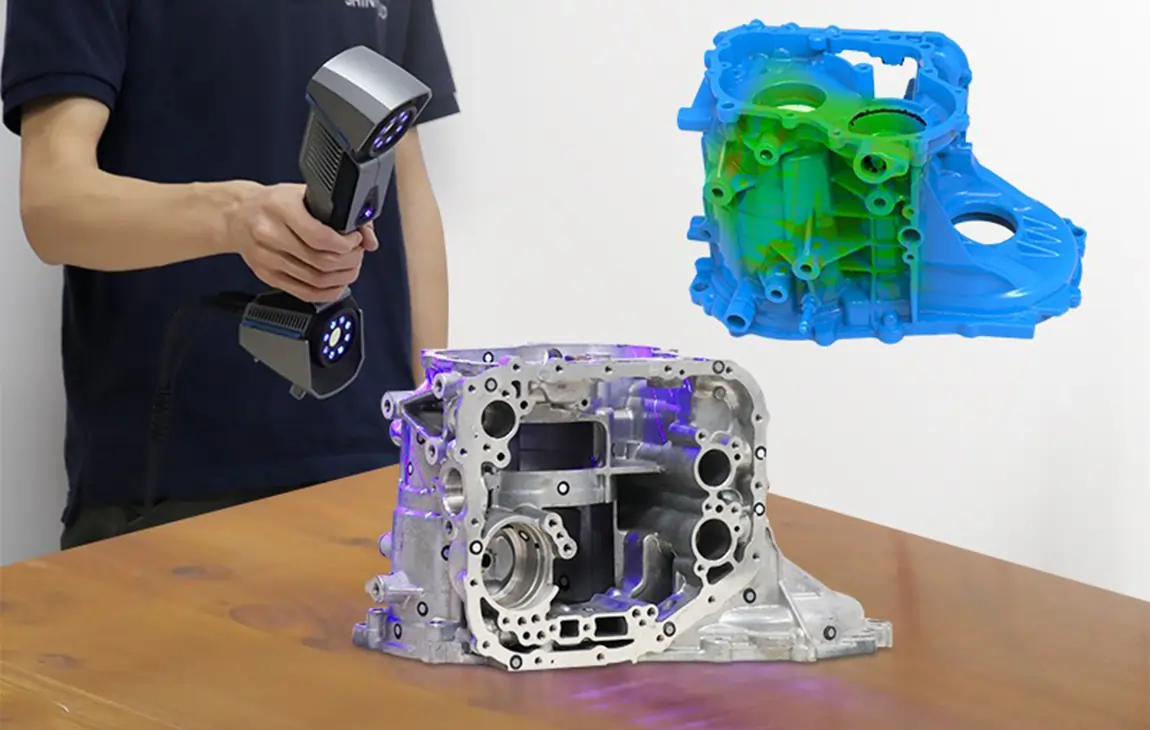
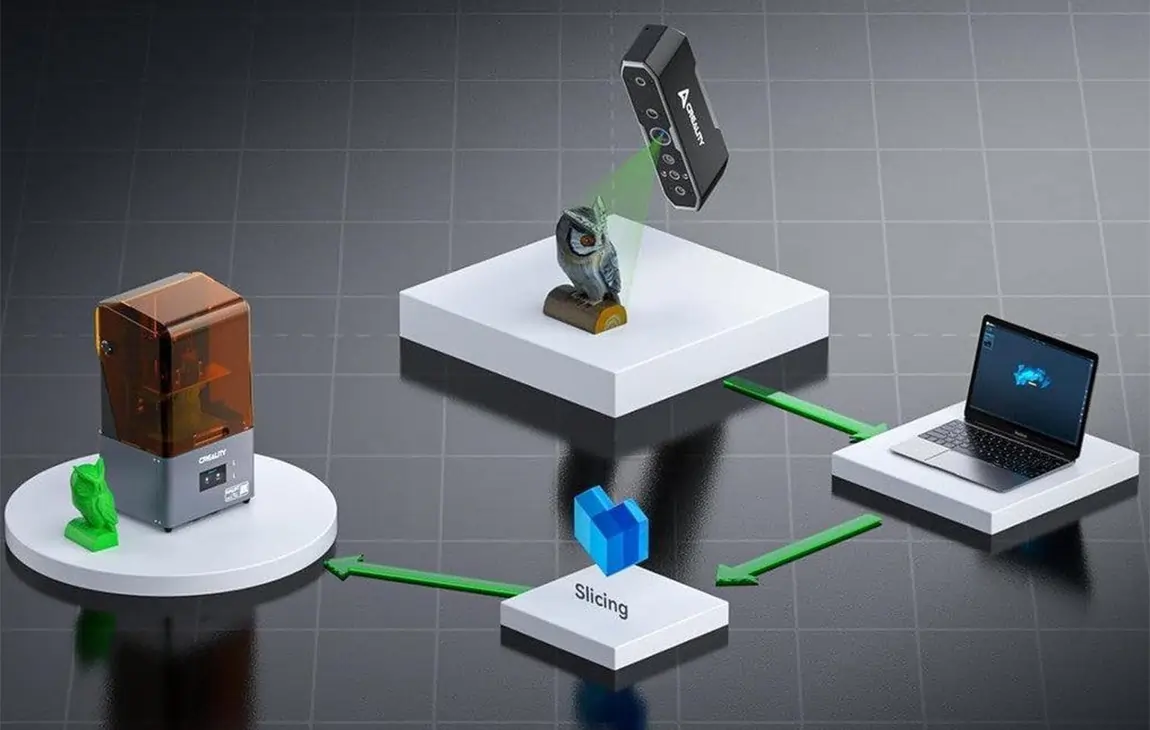
3D SCANNING / REVERSE ENGINEERING
3D scanning and reverse engineering involve using 3D scanning technology to capture the shape and dimensions of an existing object and then creating a digital model based on that data. The scanner
captures the object’s surface details, converting them into a 3D file that can be modified or analyzed.
This process is especially useful for recreating parts without existing CAD designs, repairing or improving old components, or replicating complex geometries. Reverse engineering helps in various industries, such as manufacturing, automotive, and healthcare, enabling the reproduction or enhancement of physical objects, often for prototyping, repair, or customization.
Our Creations
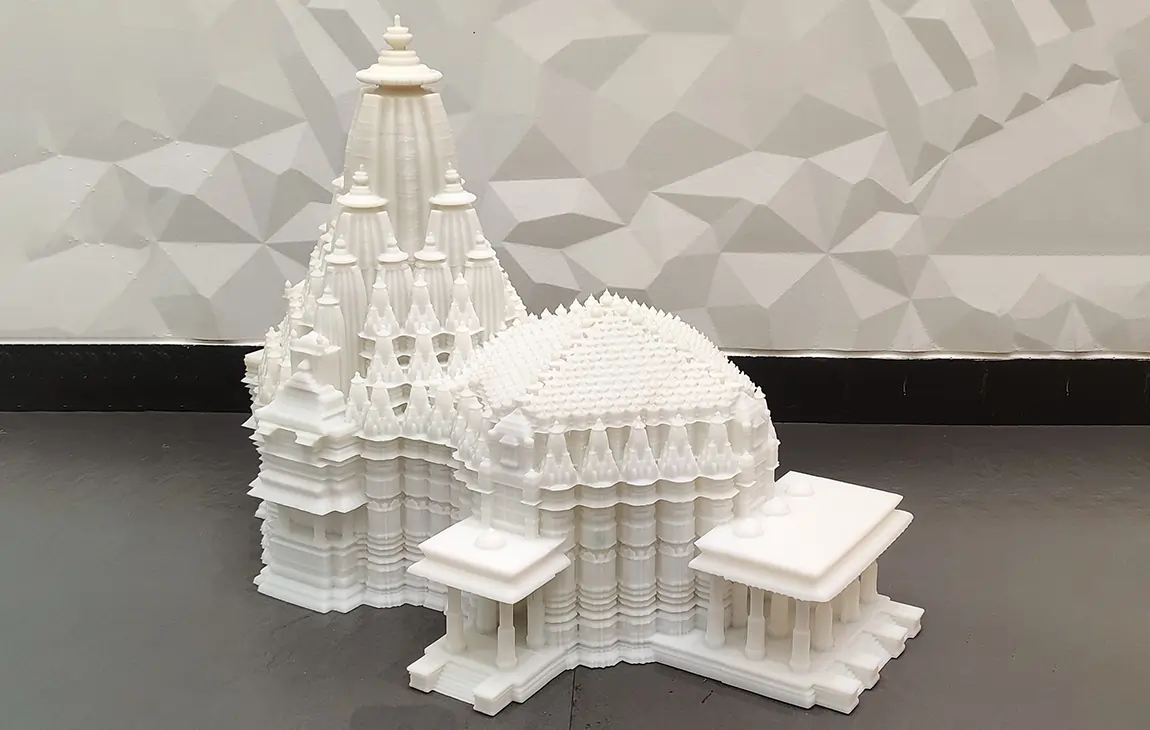
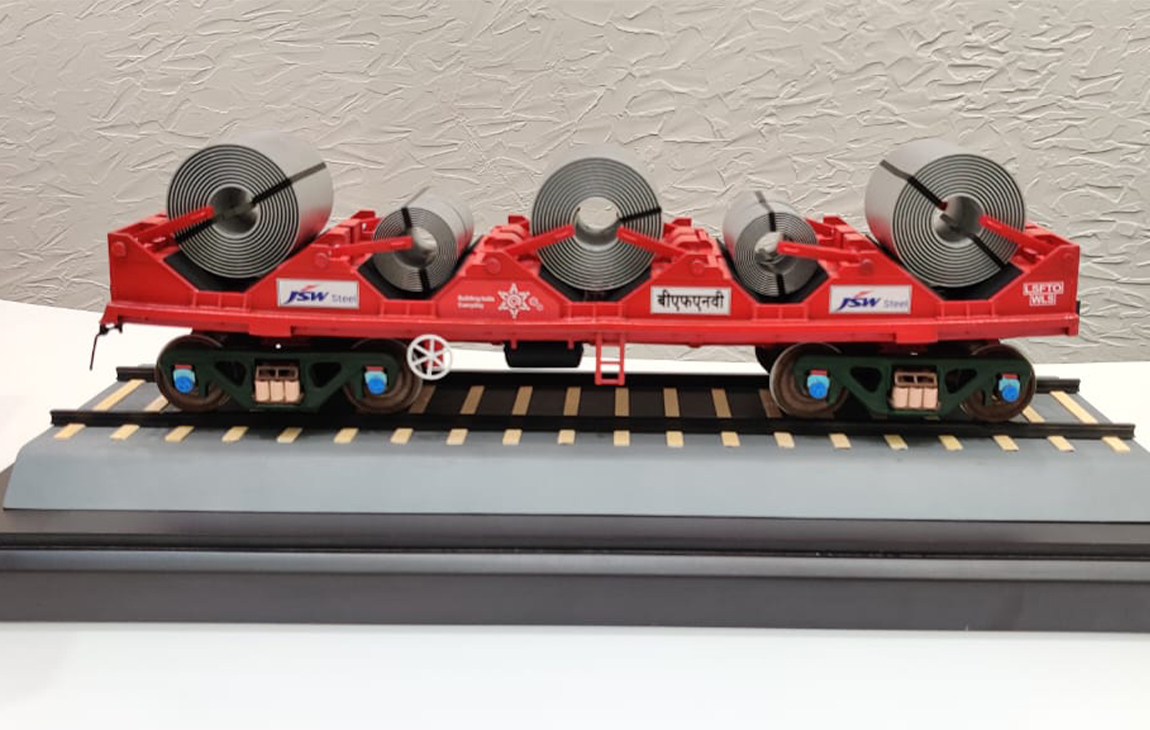
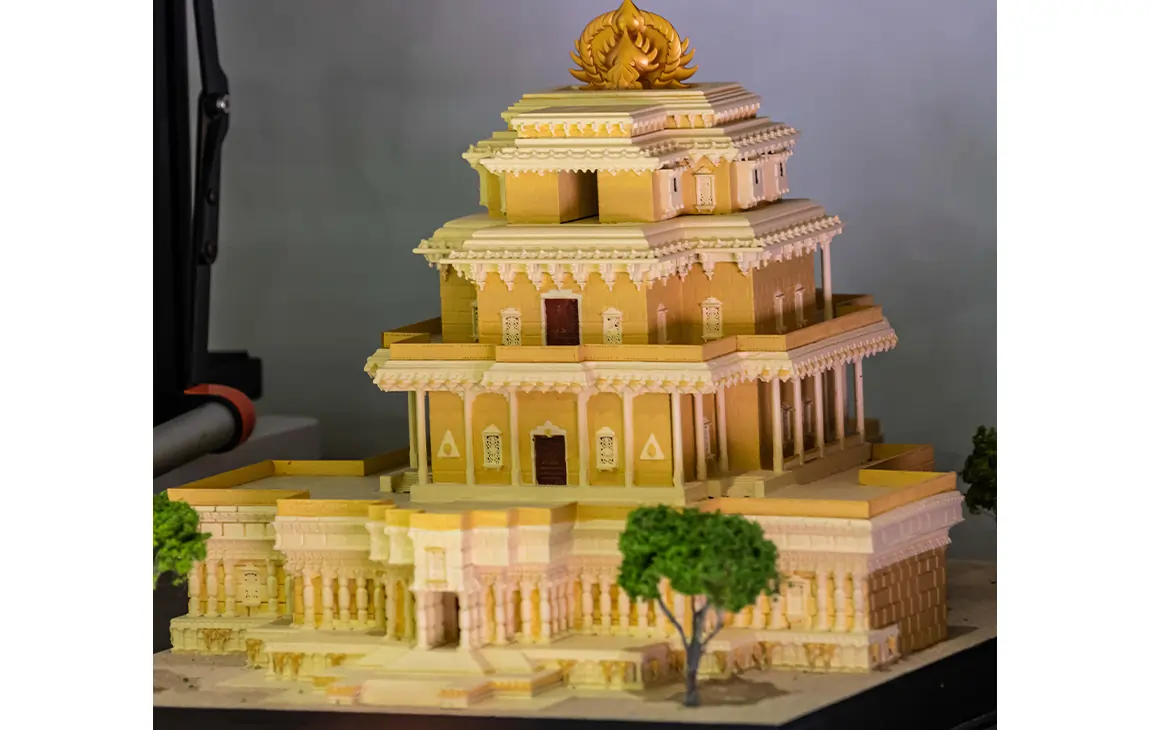
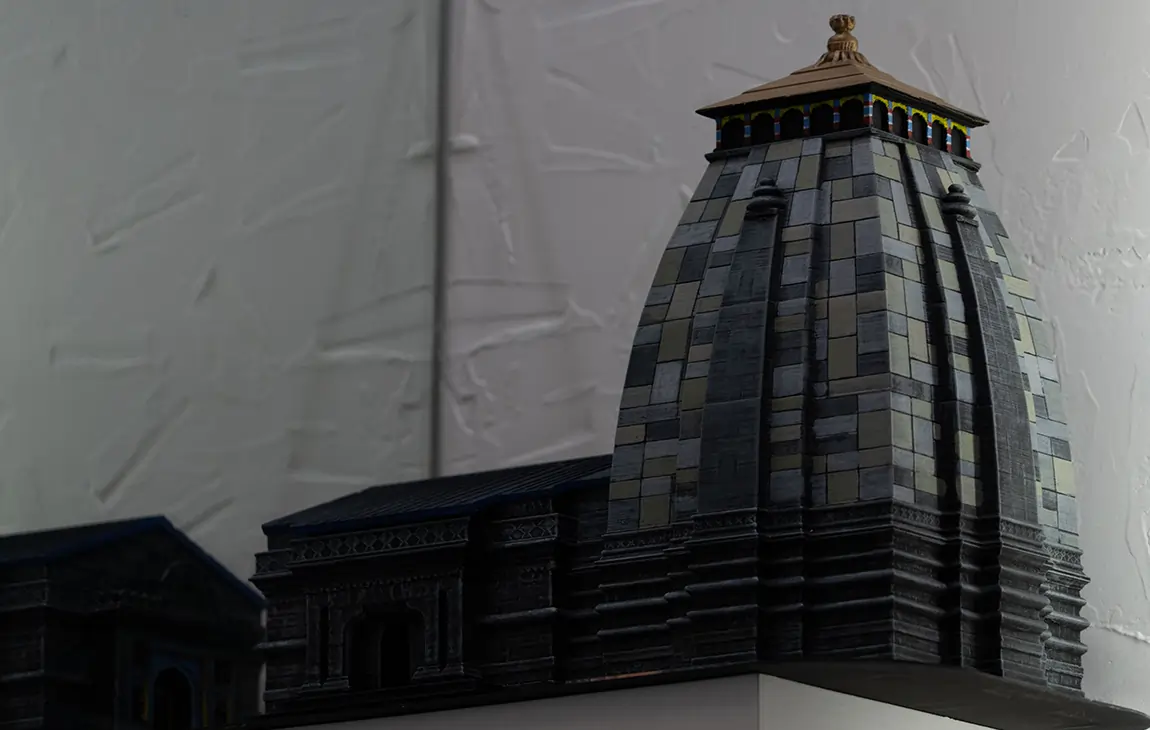
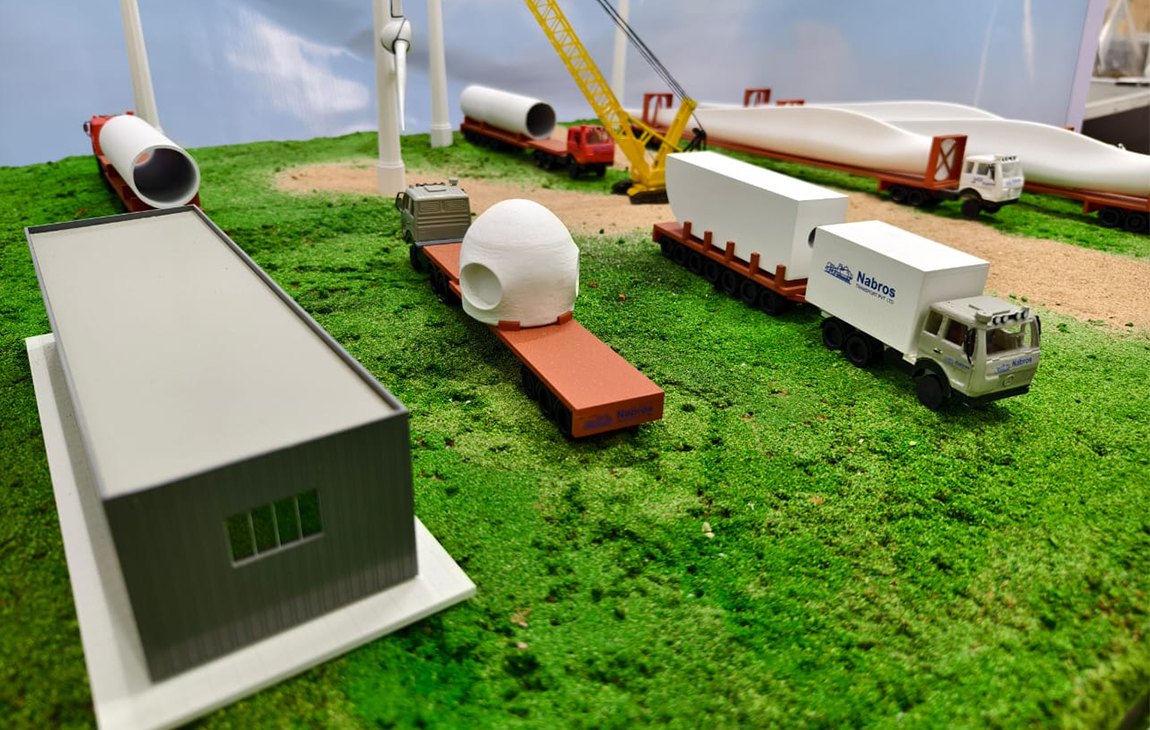
3D MINIATURE MODEL MAKING
3D miniature model making is the process of creating small-scale, detailed replicas of objects, buildings, or scenes using 3D printing technology. By using digital design files, a 3D printer can precisely layer materials like plastic or resin to build intricate models that capture fine details.
This technique is popular in industries like architecture, film production, and gaming, where miniature models are used for visualizing concepts, creating prototypes, or producing collectibles. 3D miniature models offer a high level of customization, accuracy, and realism, making them a versatile tool for both creative and practical applications.
Our Creations
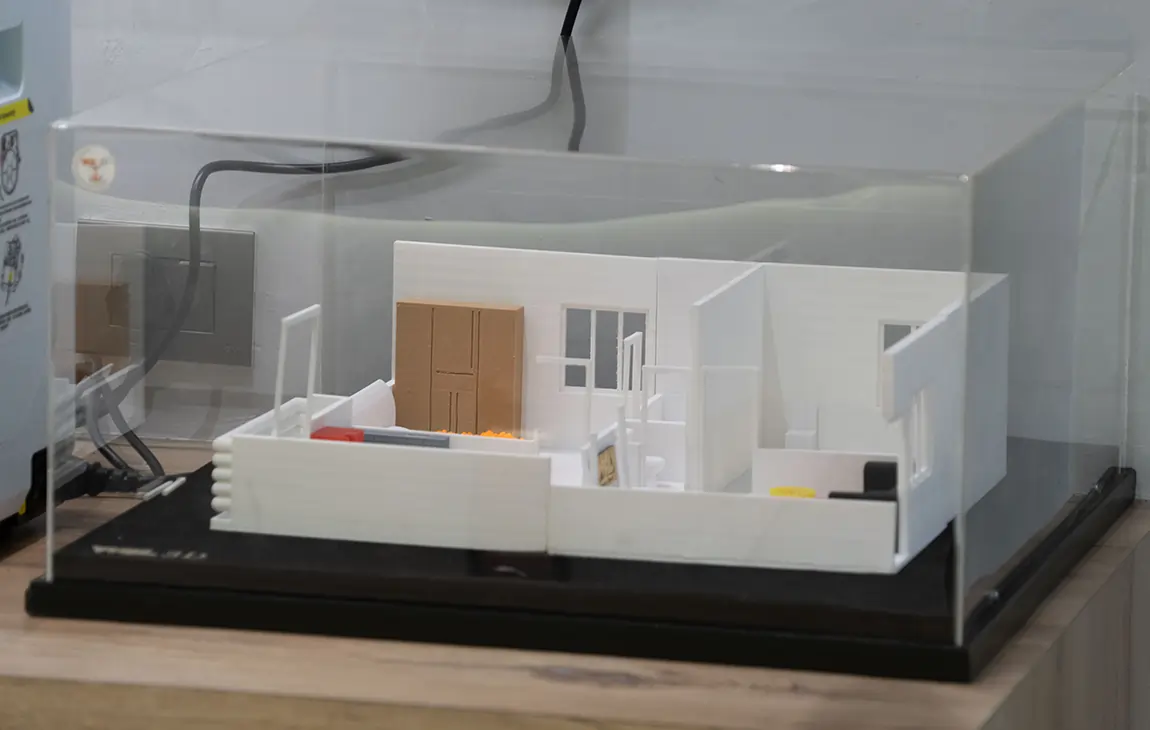
ARCHITECTURAL SCALE MODEL MAKING
Architectural scale model making is the process of creating physical, scaled-down replicas of buildings or structures to visualize and study architectural designs. These models are typically made from materials like foam, wood, plastic, or 3D-printed components, and are built to a specific scale to accurately represent the proportions and layout of the design.
Architectural models are commonly used in the planning phase to help clients, stakeholders, and design teams better understand the spatial relationships and aesthetic qualities of a project. They are also valuable for presentations, as they offer a tangible, realistic view of the final design, helping to communicate ideas more effectively.
Our Creations
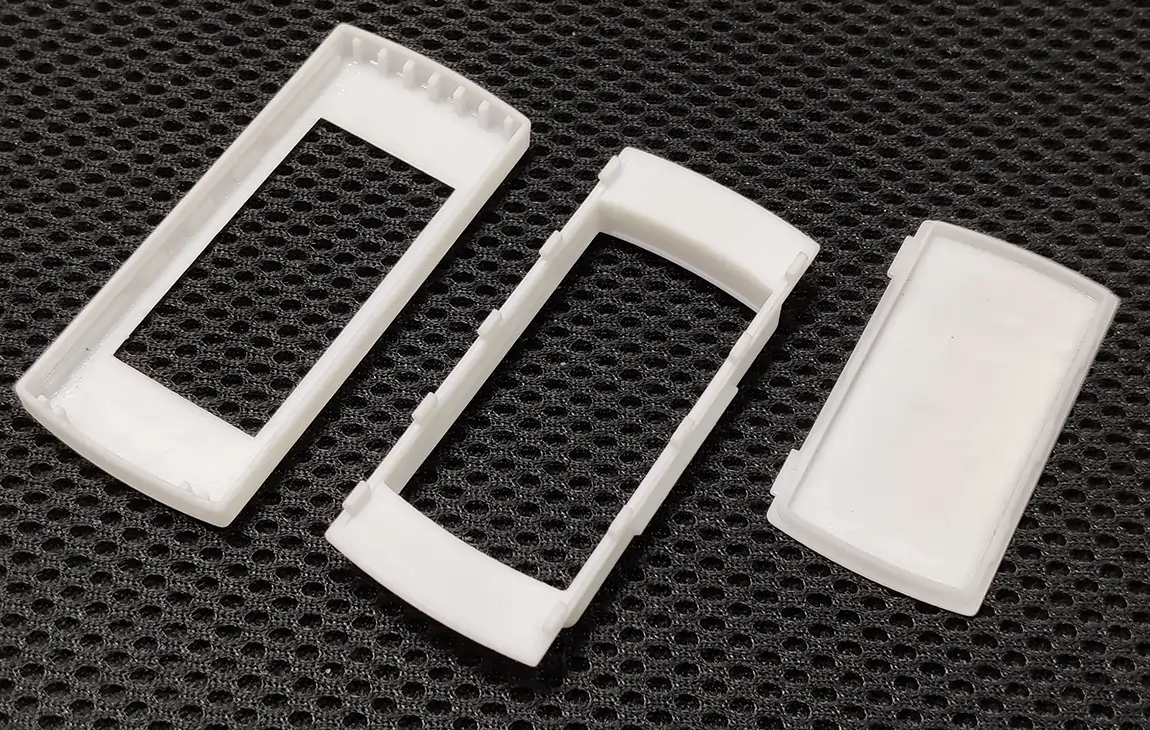
Product Designing & Development Services
Product designing and development services involve the process of creating new products or improving existing ones, from the initial concept through to production. This includes research, ideation, prototyping, and testing to ensure that the product is functional, user-friendly, and meets market needs.
These services often involve collaboration between designers, engineers, and manufacturers to refine the design and develop a product that is both innovative and manufacturable. Whether it’s for consumer goods, industrial products, or electronics, product design and development services help turn ideas into market-ready solutions, ensuring quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness throughout the entire development cycle.
Our Creations
3D MODELLING / ENGINEERING SERVICES
3D modelling and engineering services involve creating digital representations of physical objects or systems using specialized software. These models can be used for product design, prototyping, or
engineering analysis. The process includes designing detailed 3D models of parts or assemblies, simulating their behaviour under different conditions, and refining them to meet specific functional
and performance requirements.
Engineers and designers use 3D modelling to visualize concepts, optimize designs, and prepare for manufacturing. These services are crucial in industries like automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and manufacturing, as they enable precise design, cost-effective prototyping, and efficient production planning.
Our Creations
For any query contact us on +91 99675 75518/7738712329
At WOL3D 3D Prototype Services based on the design, we develop a tangible prototype. Our services will help to evaluate the look, feel, fit, and function of the product. Maybe you just need your concept printed, or maybe an idea is stuck in your head and you are not sure how to articulate it, either way, we are here to assist.